How Edge Computing is Revolutionizing the Energy Industry
How Edge Computing is Revolutionizing the Energy Industry
- Last Updated: December 2, 2024
weeve
- Last Updated: December 2, 2024



The energy industry is undergoing a significant transformation as it faces numerous challenges such as increasing demand for electricity, the integration of renewable energy sources, and the emergence of electric vehicles. One way to address these challenges is by leveraging edge computing, a distributed computing paradigm that enables the processing and analysis of data closer to the source. In this blog post, we will explore how edge computing can revolutionize the energy industry, making it more reliable, efficient, and sustainable.
The Challenges Facing the Energy Industry
The traditional power grid is one of the most critical infrastructures in our day-to-day lives. It powers our homes, schools, hospitals, and industries, among others. However, the power grid is facing numerous challenges, such as increasing demand for electricity, the integration of renewable energy sources, and the emergence of electric vehicles. These challenges require innovative solutions to optimize the grid's operation, enhance its resilience, and reduce energy waste.
What is Edge Computing?
Edge computing is a distributed computing paradigm that enables the processing and analysis of data closer to the source. It can be deployed in various locations in the power grid, such as substations, to process and analyze the data generated by the sensors in real time. Edge computing can help to optimize the power grid's operation, enhance its resilience, and reduce energy waste.
Smartening the Power Grid with Edge Computing
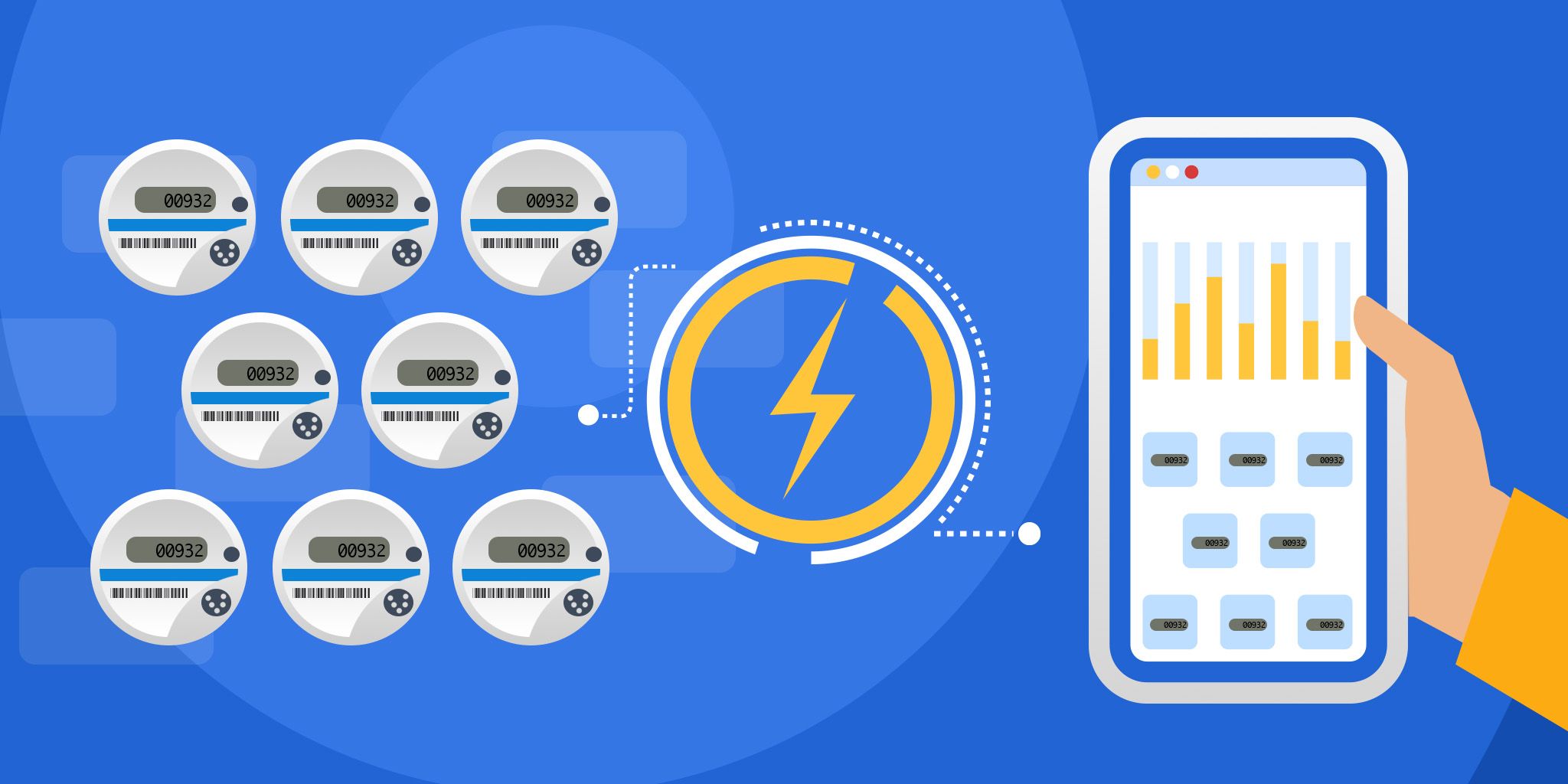
In a smart grid system, numerous sensors are deployed to collect data on the power grid's health and performance. These sensors generate vast amounts of data that must be processed and analyzed in real-time to make informed decisions. Instead of sending all this data to a centralized data center, edge computing can process the data at the network's edge, closer to the source.
"Edge computing can help to optimize the power grid's operation, enhance its resilience, and reduce energy waste."
For instance, a power utility company can deploy edge servers at various locations in the power grid, such as substations, to process and analyze the data generated by the sensors in real time. The edge servers can use machine learning algorithms to predict the power demand and supply, detect faults, and efficiently manage electricity distribution.
Edge computing can also improve the power grid's resiliency by enabling autonomous decision-making at the edge in case of network disruptions. For example, suppose a substation loses connectivity with the central control system. In that case, the edge servers can switch to a backup mode and continue to operate autonomously using the data stored locally.
The Benefits of Edge Computing
Edge computing has the potential to revolutionize the energy industry, making it more reliable, efficient, and sustainable. By leveraging edge computing, power utilities can optimize their operations, reduce energy waste, and provide higher-quality services to their customers. Edge computing can help address the challenges facing the power grid, such as increasing demand for electricity, integrating renewable energy sources, and emerging electric vehicles.
Moreover, edge computing can enable energy utilities and municipalities to create and deploy data processed quickly and efficiently, enabling them to benefit from edge computing solutions more effectively. Users with little to no programming experience can create and deploy data processes quickly and efficiently using an easy-to-use, low-code tool. This can help streamline the deployment of edge computing solutions and enable energy utilities and municipalities to address the power grid challenges more effectively.
Conclusion
The energy industry faces numerous challenges, such as increasing demand for electricity, integrating renewable energy sources, and the emergence of electric vehicles. Edge computing has the potential to revolutionize the energy industry, making it more reliable, efficient, and sustainable. By leveraging edge computing, power utilities can optimize their operations, reduce energy waste, and provide higher-quality services to their customers. Energy utilities and municipalities can benefit from edge computing and an easy-to-use low-code tool to quickly and efficiently create and deploy data processes quickly and efficiently.
The Most Comprehensive IoT Newsletter for Enterprises
Showcasing the highest-quality content, resources, news, and insights from the world of the Internet of Things. Subscribe to remain informed and up-to-date.
New Podcast Episode

IoT in 2026: Trends and Predictions
Related Articles