How Is Industrial IoT Revolutionizing the Manufacturing Industry?
How Is Industrial IoT Revolutionizing the Manufacturing Industry?
- Last Updated: December 2, 2024
Guest Writer
- Last Updated: December 2, 2024



The Internet of Things (IoT) has been booming all around the globe for a decade. The most obvious focus of IoT is the consumer domain. However, Industrial IoT (IIoT) is probably the greatest champion of this new technology.
Industrial IoT is an extension of IoT in the manufacturing industry, commonly referred to as IIoT or Industry 4.0. IIoT connects machines and industrial equipment with a secure network and enables automation in the entire industrial facility. IIoT leverages a combination of M2M communication, Big Data Analytics, SCADA, and other similar industrial equipment.
Industrial IoT may very well transform the way we look at manufacturing, but it comes with its own set of challenges, too. In this article, we take a look at both to see if all of the hype is really worthwhile.
The industrial IoT (IIoT) market for devices & technologies is expected to grow from USD 77.3 billion to USD 110.6 billion by 2025, at a CAGR of 7.4 percent during the forecast period. To understand how Industrial IoT is benefiting the Manufacturing Industry, let’s check some key points.
Benefits of IIoT
Asset Management
Imagine a factory that is manufacturing some product; the operator needs to regularly verify at what stage the product has reached, change the motor's control based on production timings, and control the production by looking at entry and exit points. In this scenario, it would be beneficial to reduce human intervention and track the assets intelligently. Smart factory systems with the help of IIoT can track asset locations with smart sensors, monitor demand-supply requirements, and manage the workflow, records, and production accordingly.
Predictive Analytics
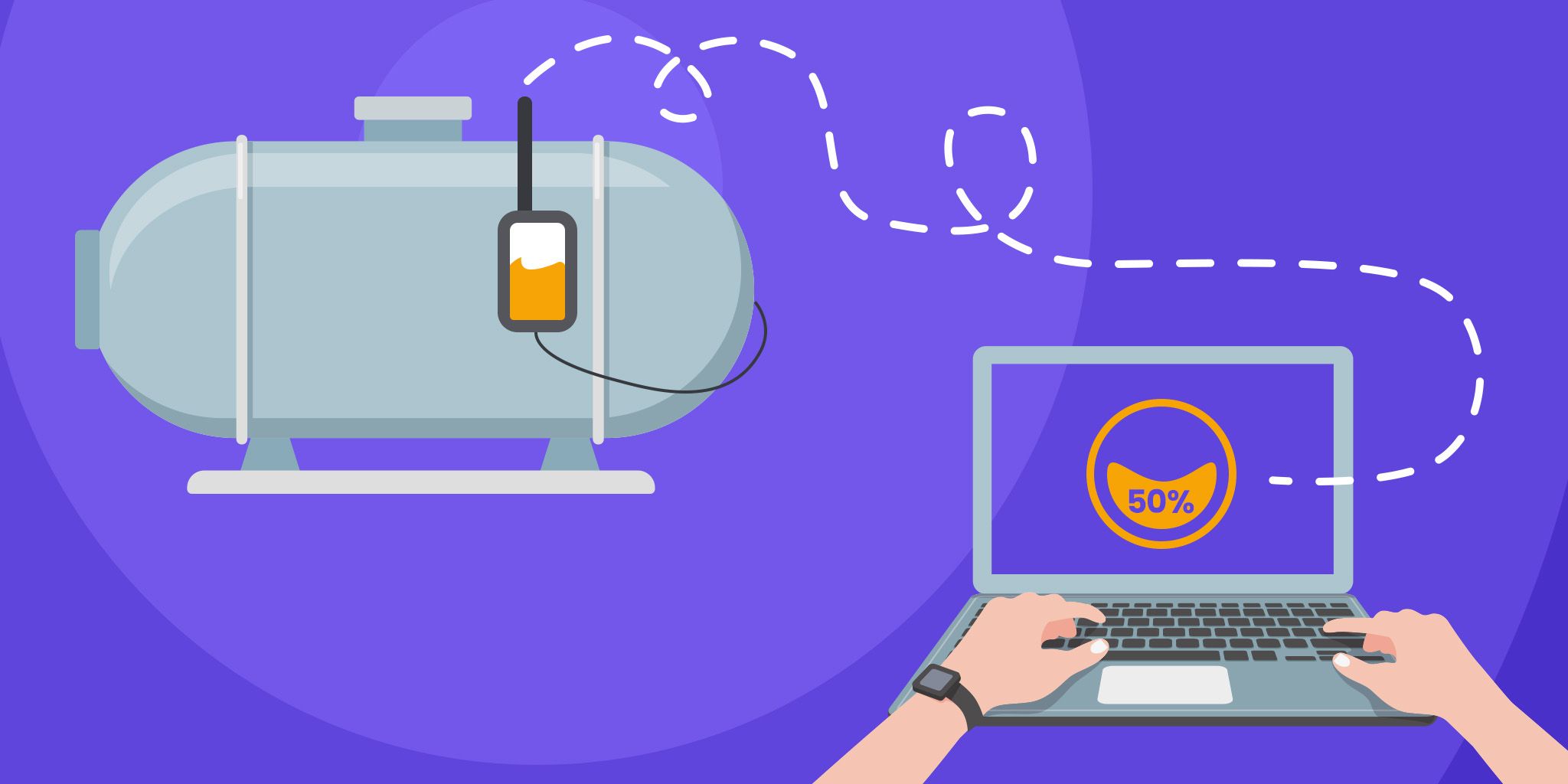
By introducing IIoT, manufacturers can better monitor equipment status, estimate the timeline required to reach certain milestones, and monitor the maintenance requirements on a machine-by-machine basis. Predictive analytics tools help engineers identify the root cause of an issue and work on the mitigation plan, thereby warning potential failures much farther in advance. As we move with this ecosystem, the production line will have more data to provide more visibility to deal with complex scenarios leading to a more robust system.
Efficient and Productive Process
Mechanical equipment in the manufacturing industry needs servicing and maintenance at regular intervals. If the equipment suffers unexpected damages, it can affect planned production and waste both time and resources. IoT-assisted production can avoid production downtime by servicing the equipment before it can lead to breakage. Eventually, production lines will see increased productivity and better decision making through enhanced analytics.
Safety Operations
Equipment in the industrial space can be hazardous, especially when it is not serviced regularly. IIoT automation units can help assure employees' safety by monitoring equipment for potentially dangerous failures and sending floor-wide alerts in the case of a potentially hazardous event.
Many manufacturing companies have started investing their time & money towards developing smart IT-driven manufacturing solutions. The adoption of Industry 4.0 enables industrial users to leverage benefits such as asset management, predictive analytics, efficient and productive processes, and safety operations. And while IIoT has definitely proven its values, it also comes with its own set of challenges in adopting manufacturers and enterprises.
Challenges of Adopting IIoT for Manufacturers and OEMs
Interoperability
The manufacturing processes involved in different sectors vary. There are neither standards nor sets of industrial smart sensors for the industrial sectors available. For example, transferring data between machines from different vendors within an ecosystem may prove a challenge. Standards like Zigbee and Thread have enabled greater interoperability between devices, but similar standards have not been set for Industry 4.0. OEMs and SMEs will need to change/digitize their process to ensure the business unit's interoperability based on existing processes.
Security
Ensuring smart technology is pointless if it does not have an interconnected system. However, connecting industry-grade machines with a network carries risks. It can lead to vulnerabilities and can cause malfunction of the manufacturing process, potentially putting the safety of employees and machines at stake. It is a must for Industry 4.0 OEM to have the most robust and secure environment possible to protect from cyber threats.
Insufficient Expertise Amongst Industry Makers
As IIoT is still in the early stages, some industry skills are still lacking or hard to find. Things like coordinating hardware, integrating data from various sources, and vendors' realization can all prove challenging. Small scale companies will find it difficult to get started with Industry 4.0 technology due to lack of knowledge and huge investment requirements.
Lack of Proven Technology
A smart manufacturing unit will need to have a mechanism or sensors that detect and collaborate data from one machine to another. This requires industry-grade sensors and smart devices or equipment. Currently, there isn't a great range of smart sensors and machines in the market. And developing industry-grade sensors requires extensive training and simulation within the ecosystem, which can prove difficult, especially for cash-strapped companies.
IIoT Architecture
We've reviewed some of the benefits and challenges of implementing IIoT–– now let's go through some of the architecture of an IIoT system.
Industrial IoT Gateway
An industrial gateway interfaced with PLC, DCS, and other data collection sensors via OPC UA or some other industry standards. It will support the cloud, which helps to connect the real things with the digital world. Cloud-based gateway will enable an analysis of production data that will drive core business logic.
Key Features
- Cloud connectivity via reliable high-speed ethernet, Wi-Fi, or LTE connectivity (for very remote areas)
- Supports standard industrial protocols (Modbus, OPC Unified Architecture -OPC UA, MTConnect, etc.)
- Integration with PLC and SCADA
- Time-sensitive networking (TSN)
- Sends important data to the cloud for big data analysis and predictive maintenance
Use of Smart Manufacturing Solution
A smart manufacturing solution would help manage manufacturing units in a phase-wise manner and provide failure reports for assets. This solution will also support industrial motor control and speed diagnostics. To track and to control manufacturing remotely, this solution would provide a cloud interface.
Key Features
- Control the operations and speed of the motors
- Temperature and pressure measurement and analysis
- Take appropriate actions on hitting the threshold values of temperature and pressure
- Manufacturing phase-wise tracking with Rain-RFIDs and location plotting
- Inventory management and order more stock/component when necessary
- Cloud connectivity via reliable high-speed ethernet, WiFi or LTE connectivity (for remote areas) and manufacturing statistics
The Most Comprehensive IoT Newsletter for Enterprises
Showcasing the highest-quality content, resources, news, and insights from the world of the Internet of Things. Subscribe to remain informed and up-to-date.
New Podcast Episode

Navigating the Future of Embedded Computing
Related Articles