A Simple Guide to the Types of Industrial Maintenance
A Simple Guide to the Types of Industrial Maintenance
- Last Updated: December 2, 2024
Yalantis
- Last Updated: December 2, 2024



IoT technologies continue to be incorporated into our everyday lives and all spheres of business. Large-scale manufacturing is no exception. IoT is presenting ways to make the types of industrial maintenance available today better.
Bsquare conducted a survey back in 2017 and found that 86 percent of high-level market participants across several industries were already implementing IoT solutions in some form. Another 12 percent planned to implement IoT in their workflow in the near future. As soon as major market players learned how the Internet of Things could be used in manufacturing (and its benefits), its worldwide adoption became a question of time.
There is also increasing assuredness in industrial IoT among top executives; a survey by PwC in 2019 showed that 93 percent of respondents believed that the benefits of implementing IoT outweighed the risks. Moreover, 70 percent of respondents had already established or were developing IoT projects in their enterprises. These numbers show that the IoT trend has gained serious momentum. However, many manufacturers are still overlooking the benefits of implementing IoT for effective equipment maintenance.
Our goal today is to bring you clear and comprehensive information on the kinds of manufacturing maintenance and why it is important to implement IoT in the maintenance process.
There is increasing confidence in industrial IoT among top executives. However, many manufacturers are still overlooking the benefits of implementing IoT for effective equipment maintenance.
Types of Maintenance
Manufacturing equipment must always be ready for work. If it isn’t, it can ruin a business in no time. It doesn’t matter what industry you’re in, time losses turn into monetary losses at an accelerating rate. Not only does a company lose potential gains from work that equipment can’t perform and money spent on repairs; there are other potentially serious problems stemming from broken-down equipment:
- Government sanctions. A lot of big manufacturing companies deal with problems of environmental pollution, creating situations dangerous for health, or other public threats. If they fail to prevent such problems, governments may take stern measures. For instance, a manufacturer may lose a lot of money if their water treatment equipment fails or may lose a drug manufacturing license if there are malfunctions in their pharmaceuticals production line.
- Loss of partners. In business relationships, one has to meet obligations and do so in due time. Some business partners might be willing to gloss over one failure, but a company might easily lose a partnership.
- Global reputational losses. The inability to perform an expected activity is a huge minus for a company’s reputation in the business community. Everything is in the open, and a history of equipment failures can turn away a lot of potential partners and affiliates.
In light of this, any large manufacturer should strive to improve its maintenance routine. We’ll look at the types of maintenance used today and their ability to keep the production line healthy.
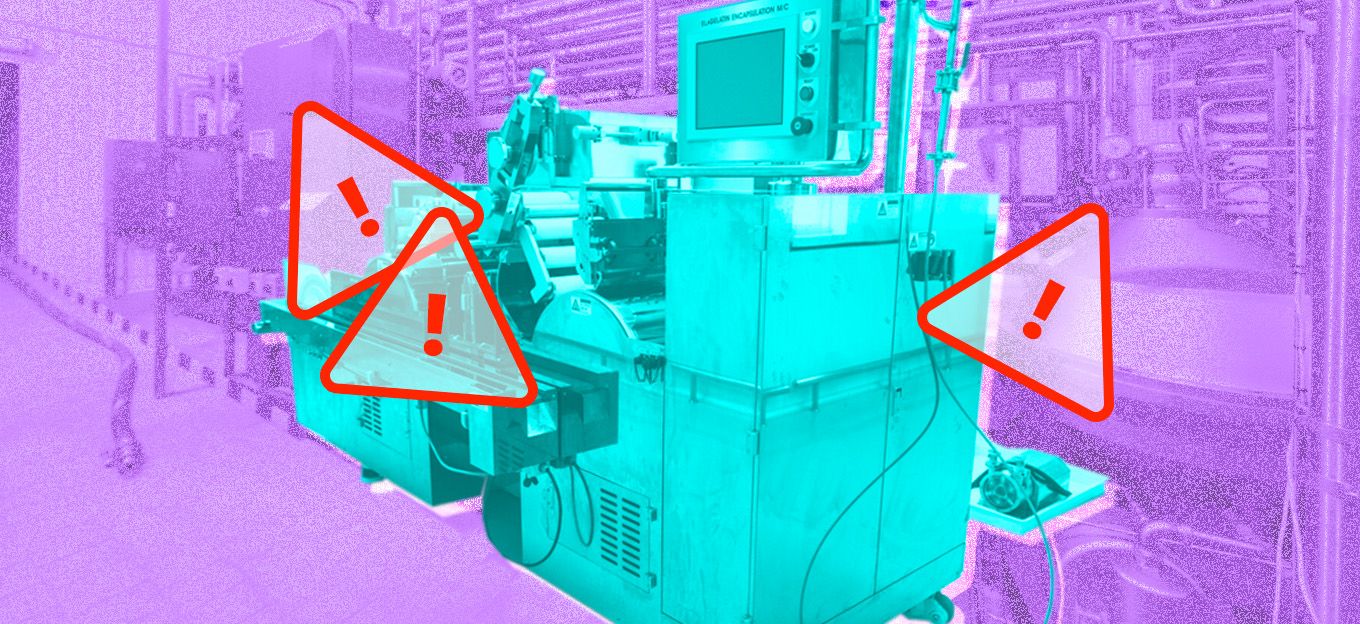
Reactive Maintenance
The most established and common kind of maintenance, reactive maintenance is dealing with equipment failures after they occur. Reactive maintenance is widely used but poses a lot of danger to any company.
A good case to illustrate how dangerous reactive maintenance can be is the Visakhapatnam gas leak incident. An LG Polymers-owned chemical plant near Visakhapatnam, India, had a serious gas leak in May 2020. The local population took a disastrous hit, with 11 people dead and more than 1,000 poisoned by gas exposure. The leak also completely broke the supply of drinking water in the region, and more than 20,000 people had to be evacuated.
The consequences for LG Polymers were serious. The CEO, technical director, managing director, and nine other personnel faced charges. The company also had to pay $7 million initially to mollify the harm done.
A set of temperature sensors installed on gas tanks in the plant and connected to an IoT system could have completely avoided this disaster.
It doesn’t matter how fast and efficient maintenance crews are if a failure brings such consequences as in the Visakhapatnam case. Reactive maintenance is not sufficient for an enterprise that strives to reach its top efficiency.

Source: Yalantis
Preventive Maintenance
Preventive maintenance doesn’t require complex technological solutions and still provides somewhat better results than a fully reactive approach. The core of this method is a schedule of maintenance sessions. The interval between sessions must be short to allow for noticing and preventing most potential problems. Still, preventive maintenance is far from perfect: there are a plethora of problems that arise abruptly and leave no time for maintenance crews to notice and react to them.
Moreover, the more frequent maintenance checks are, the more money and time a company has to spend on them. With preventive maintenance, a company will have to spend a lot to keep their manufacturing even relatively safe.

Source: Yalantis
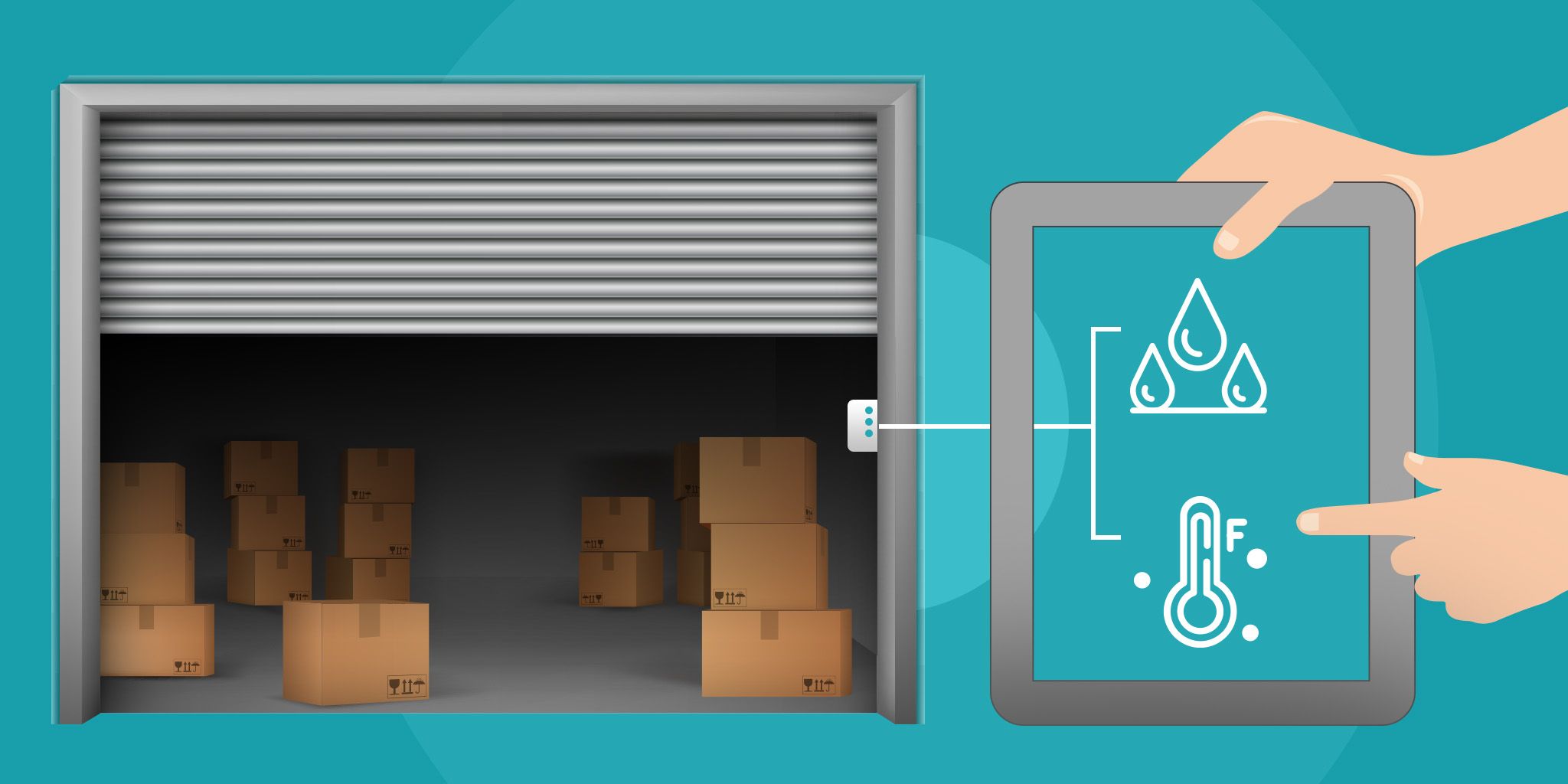
Condition-Based Maintenance
Special sensors are used in this kind of maintenance. They track the degree of equipment degradation and send signals to the person responsible when a critical level is reached. Condition-based maintenance is a huge step forward in comparison to reactive and preventive maintenance, but it has some drawbacks too, the most important being a lack of precision. A signal is sent only when equipment is in a dire condition, which is not ideal for maximizing maintenance efficiency.

Source: Yalantis
Predictive maintenance
Predictive maintenance is the modern maintenance ideal. It uses IoT technology for precise and constant equipment monitoring that allows for early detection of most potential failures. Predictive maintenance uses an array of sensors connected to a system of devices dedicated to processing and analyzing those sensors’ signals.
Sensors gather all kinds of information important for recognizing the state of equipment and potential problems, and processing devices allow you to track that information in real-time and administer required measures. Algorithms built into the system present all data in the form of easy-to-read reports, charts, and graphs.
Predictive industrial maintenance integrated automation allows manufacturers to act preemptively and deal with problems before they have a chance to hurt the enterprise. Predictive maintenance provides immense monetary, legal, and reputational protection and offers a big contrast to the reactive approach.

Source: Yalantis
There is much more to predictive maintenance software. It’s a complex topic. There is much more that could be said here, such as who could benefit from predictive maintenance and real-world applications. However, this brief overview lays out the different approaches to industrial maintenance used today. IoT will continue to enhance maintenance strategies, making predictive maintenance more acheivable for organizations.
The Most Comprehensive IoT Newsletter for Enterprises
Showcasing the highest-quality content, resources, news, and insights from the world of the Internet of Things. Subscribe to remain informed and up-to-date.
New Podcast Episode

IoT in 2026: Trends and Predictions
Related Articles