7 Ways Smart Agriculture Lowers Food Prices
7 Ways Smart Agriculture Lowers Food Prices
- Last Updated: December 2, 2024
Zac Amos
- Last Updated: December 2, 2024



Reducing food costs ensures food security and affordability for consumers worldwide. Lowering these costs can help mitigate hunger, improve nutrition, and boost economic stability, especially in low-income regions. Smart agriculture has the potential to revolutionize the industry.
The Internet of Things (IoT) is pivotal in transforming agriculture by introducing innovative solutions that enhance efficiency, productivity, and sustainability. Technological advancements enable farmers to produce more with fewer resources, driving down the cost of food and making it more accessible to everyone.
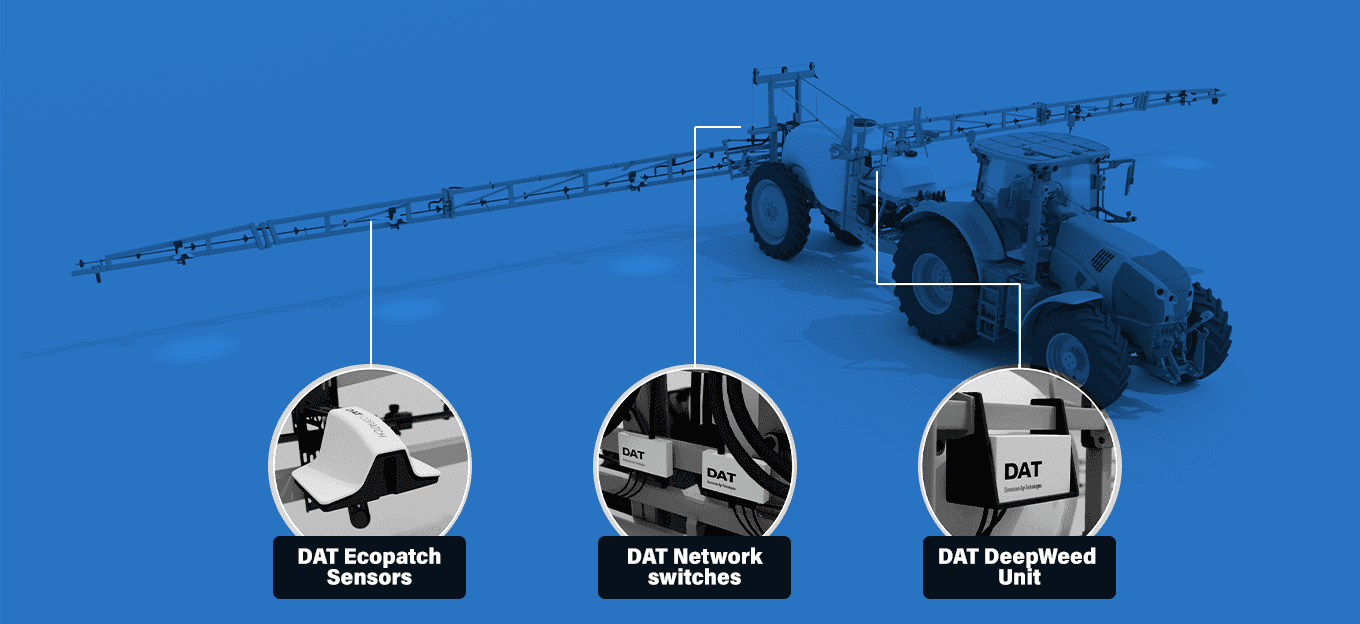
1. Precision Smart Agriculture
GPS and IoT devices in smart agriculture have revolutionized field-level management by offering farmers precise control over their operations. Input costs such as seeds, fertilizers, and pesticides have skyrocketed, rising between 80% and 250% in recent years. By leveraging GPS technology, farmers can map their fields accurately, apply inputs only where needed, and reduce waste.
Meanwhile, IoT devices provide real-time data on soil moisture, weather conditions, and crop health to allow more informed decision-making. These advancements help cut input costs and increase yields by ensuring optimal growing conditions and efficient resource use.
2. Drones and Aerial Imaging
Drones have become an invaluable tool in smart agriculture, as they enhance crop monitoring, planting, and spraying processes. With advanced imaging and sensor technology, drones can provide detailed aerial views of fields. Farmers can monitor crop health, detect diseases, and assess water and nutrient needs.
For planting, drones can precisely sow seeds across large areas to ensure uniform distribution and optimal plant spacing. When spraying, drones deliver inputs such as fertilizers and pesticides exactly where needed. This precise application minimizes waste and environmental impact, improves crop yields, and reduces labor costs by automating tasks that traditionally required extensive manual effort.
3. Blockchain and Supply Chain Optimization
Using blockchain technology in smart agriculture transforms the supply chain by enhancing traceability and transparency. Blockchains record every transaction detail — from farm to table — and lock this information into a secure, immutable ledger. This makes committing fraud challenging, as any attempt to alter the data is immediately evident.
With every supply chain step visible and verifiable, farmers and distributors can more efficiently manage logistics and reduce delays and errors. This improved coordination cuts food waste because stakeholders track and manage products more precisely. Additionally, blockchain technology contributes to lower transportation costs by optimizing transportation routes and ensuring timely deliveries.
4. Automated Machinery and Robotics
Autonomous tractors and harvesters revolutionize the agricultural landscape by significantly increasing efficiency and productivity. These advanced machines have GPS, sensors, and artificial intelligence, enabling them to operate with minimal human intervention. These autonomous vehicles reduce the need for manual labor by automating tasks such as plowing, planting, and harvesting.
Additionally, they work with remarkable precision, which minimizes human error and ensures consistent performance. This technological leap allows farmers to manage larger fields more effectively, optimize resource use, and enhance crop yields while maintaining high safety and accuracy standards.
5. Smart Irrigation Systems
Sensor-based irrigation systems improve water management in smart agriculture by enabling precise water usage tailored to each crop's specific needs. These systems utilize real-time data from soil moisture sensors to determine the exact amount of water required, ensuring crops receive optimal hydration without waste. This precision in water application conserves this vital resource and reduces utility costs for farmers.
Moreover, maintaining ideal soil moisture levels enhances crop yields and increases agriculture productivity. As rising food prices have also driven up land prices, the efficiency of sensor-based irrigation systems helps farmers maximize their output from increasingly valuable farmland. This practice makes sustainable agriculture more economically viable.
6. Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology
Developing high-yield, pest-resistant, and drought-tolerant corps is a significant breakthrough in smart agriculture biotechnology. These genetically engineered crops thrive in challenging conditions and reduce the need for chemical interventions. With farmers using over 1 billion pounds of pesticides annually in the U.S., these advanced crops offer a sustainable alternative by inherently resisting pests and diseases.
Moreover, their enhanced drought tolerance ensures stable production even in water-scarce regions, which increases crop productivity. These innovations improve food security and support farmers in achieving higher yields with fewer resources. They promote a more sustainable and efficient agricultural system.
7. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
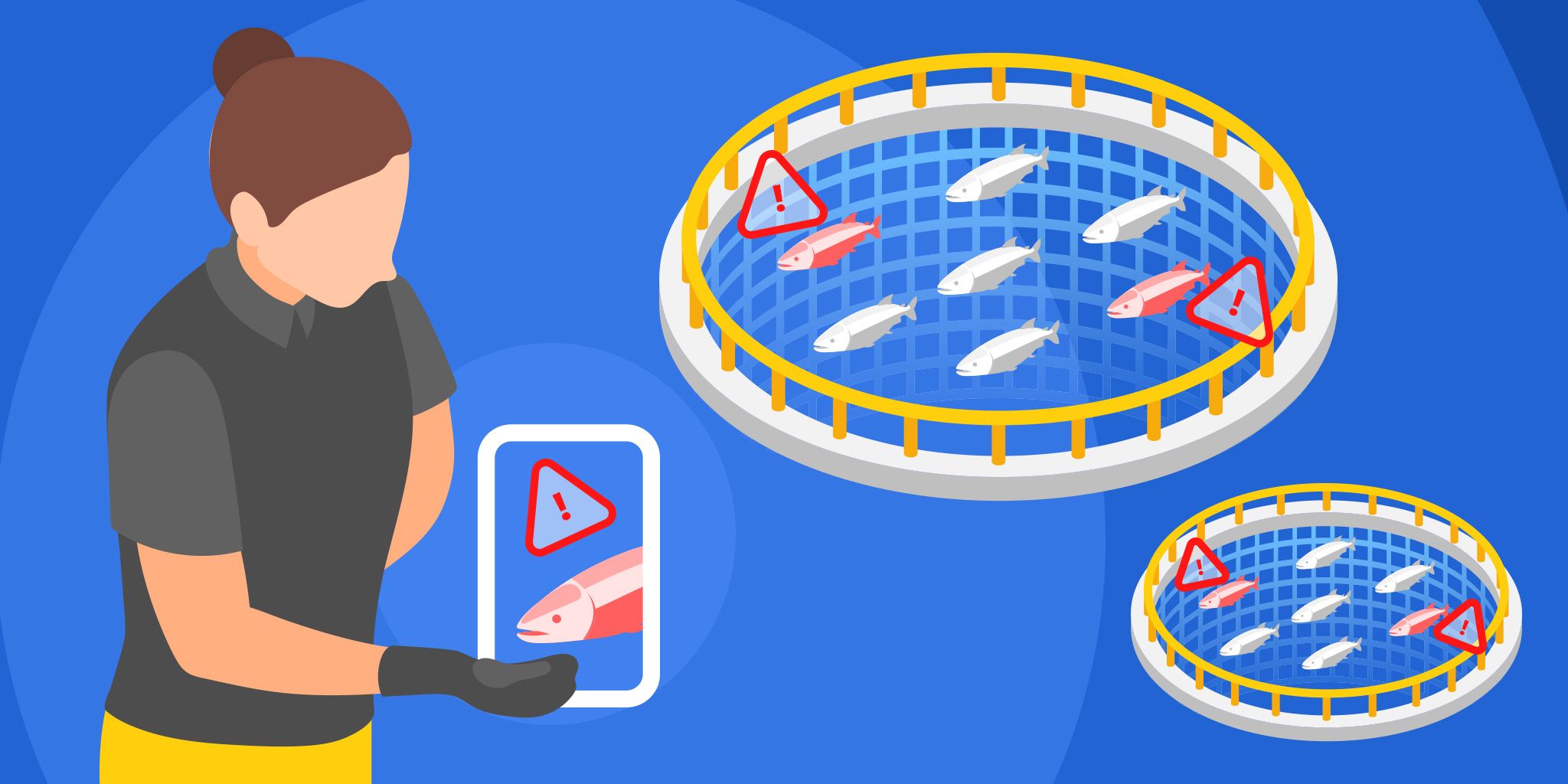
AI-driven predictive analytics transform crop management and disease detection by providing detailed insights that were previously unimaginable. With AI, a single plant can generate millions of data points, capturing how variations in light, water, weather, and other environmental factors impact production, disease, and waste. This vast data identifies potential problems early and allows farmers to address issues before they escalate.
Moreover, AI tools optimize resource use by tailoring inputs precisely to the crop’s needs. This accuracy ensures efficient water, fertilizer, and pesticide application. Likewise, it enhances crop health and yields and reduces waste and operational costs, which makes farming more sustainable and profitable.
Collective Impact of Smart Agriculture
These advanced smart agricultural IoT technologies collectively reduce food costs by increasing efficiency, optimizing resource use, and enhancing crop yields while minimizing waste and labor expenses. The future of agtech promises extraordinary advancements, ensures sustainable practices, and improves food affordability for consumers worldwide.
The Most Comprehensive IoT Newsletter for Enterprises
Showcasing the highest-quality content, resources, news, and insights from the world of the Internet of Things. Subscribe to remain informed and up-to-date.
New Podcast Episode

Navigating the Future of Embedded Computing
Related Articles