AI is the Foundation of Autonomous Vehicles
AI is the Foundation of Autonomous Vehicles
- Last Updated: December 2, 2024
Guest Writer
- Last Updated: December 2, 2024



Autonomous cars have been recently hitting the headlines and dominating tech-talks. It's being seen as a post-Uber disruption to public commute and transportation of goods. It's surely not a figment of the imagination in the age of artificial intelligence (AI) which is being used to complement driverless cars. The combined might of AI and driverless technologies is a formidable force to reckon.
The likes of Waymo, Tesla, etc. are heavily invested in driverless cars. In fact, Waymo has been testing its driverless car in Phoenix, Arizona, with the intent to start operation by the end of 2018. Tesla has already implemented a couple of “autopiloting” features in its cars.
But, before we get into further details, let's discuss what autonomous means. There are various levels of vehicle automation:
- Automation for driver assistance - It's a preliminary level or starting point of car automation where the system assists the driver but does not take control of the car. E.g. parking sensors.
- Partially automated driving – The system takes partial control, but the driver is primarily responsible for the operation of the vehicle.
- Highly automated driving – Allows users to let the system take control of the vehicle for a longer duration of time. E.g. on the highway.
- Fully automated driving – The system is responsible for driving the vehicle without interference from any human. However, the human presence is still needed.
- Completely automated car – The vehicle can completely navigate its way through from one point to another without any assistance from a driver.
Depending on the level of automation, the definition of autonomous also varies. While automation for driver assistance and partially automated cars are in commercial use, the remaining stages are still under test conditions.
For us to achieve the remaining stages of automation, or even come close, AI is the stimulus that's being used. For the purpose of this article, let's discuss the impact of AI in "highly automated," "fully automated" and "completely automated" vehicles, and how the power of AI is being harnessed to bring it to reality.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Complementing the Use of Autonomous Cars
Subject to regulatory and social acceptance, the impact of completely autonomous cars isn't limited to the disruption of only the public transport system. From a macro level, it impacts urbanization, township planning, food delivery and possibly shakes the ever-increasing real-estate market.
For AI to work, it needs IoT devices (such as radars, ultrasound, radar, cameras, LiDAR, accelerometers and gyroscopes) that augment real-time operating environments and positioning of the vehicle.
Having discussed the potential of AI, let’s talk about the top four areas where AI is being seen as a gamechanger towards the success of autonomous vehicles.
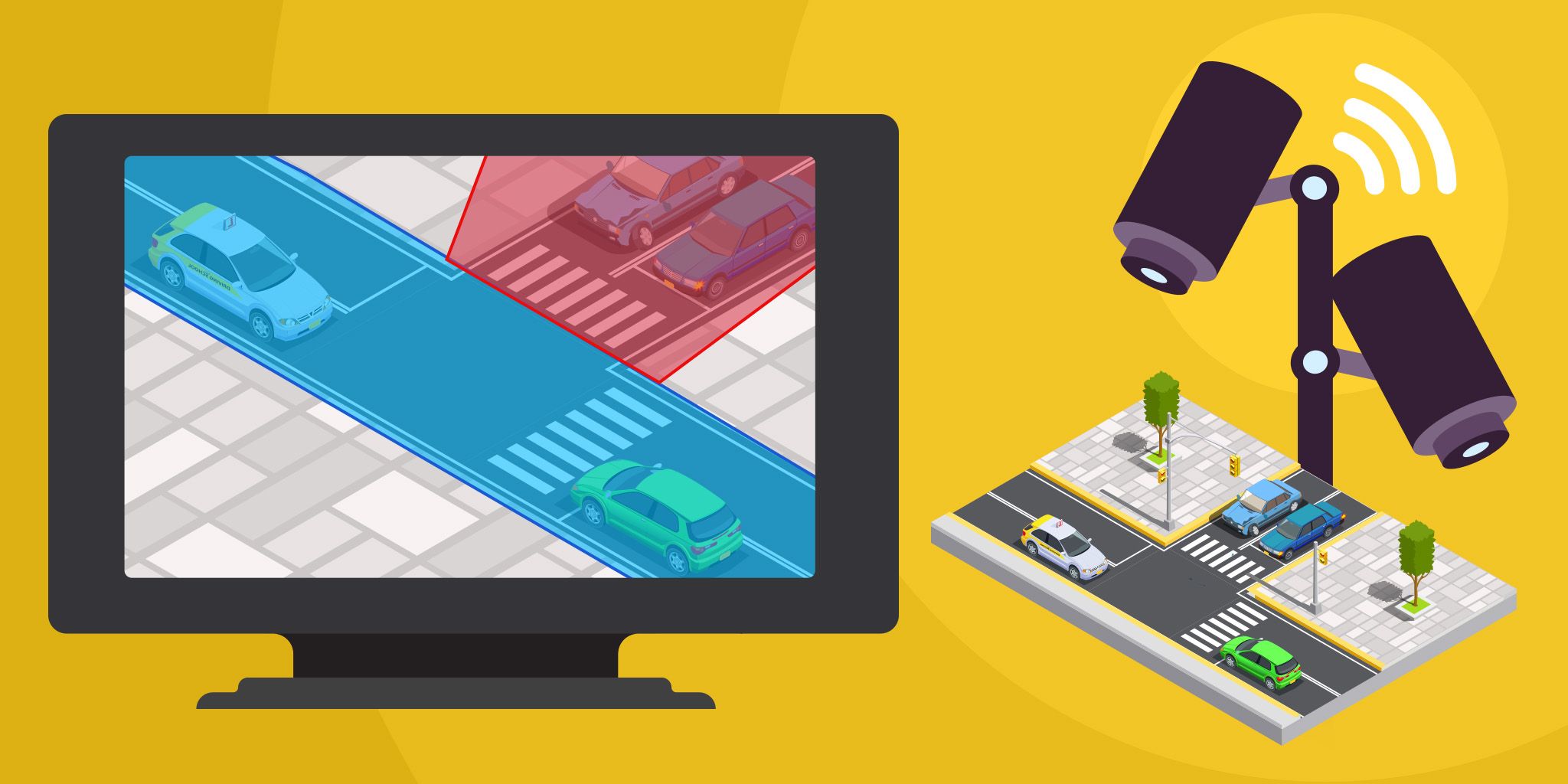
1. AI for Self-Driving Car Safety
Before AI completely takes over the driver’s seat, it's being used as a co-pilot to gain the confidence of the users, regulators and manufacturers. By analyzing data feeds across its sensors, AI can be handy in situations where flesh and blood drivers are prone to making human errors.
AI can score very highly in areas such as:
- Emergency control of the vehicle
- Cross-traffic detection
- Syncing with traffic signals
- Breaking in cases of emergencies
- Active monitoring of blind spots
- Assisting the driver in case he or she is distracted
The amount of processing power needed to drive a vehicle is enormous, and you don't have control over the external environment, which has countless variables – it needs to learn a lot. There are numerous companies testing AI’s application in driving, but the most noteworthy achievements have been made by Waymo and Tesla.
Waymo’s AI algorithms are fed with real-time data from sensors, GPS, radar, lidar, cameras and cloud services. These data are processed to produce control signals that are used to operate the car.
The world is changing faster than imagined, and AI is getting smarter with every passing day. Autonomous cars have been recently hitting the headlines and dominating tech-talks.
2. Curated Cloud Services Targeted for Individuals
AI can be used to accurately gauge the physical condition of the vehicle. Data gathered from the usage can be processed for both predictive and prescriptive maintenance.
3. Accurate Feed for Regulators and Insurance Companies
Data from automated cars can be used to determine traffic violations and claims. From an insurance perspective, AI can be of help to determine:
- Driver risk assessment – Using AI, a driver’s behavior can be accurately gauged, and, based on the risk profile, the premium can be charged.
- Ease of claims – Data from the vehicle and can be used for faster processing of claims in case of accidents. E.g. Art Financial’s AI-based video app Dingsunbao 2.0 allows users to access their auto damage.
4. Monitoring Driver and User Behavior
The application of AI in autonomous cars isn't limited to stricter requirements such as safety but also fills the fun quotient. AI can be used for a host of infotainment features in the car.
User behavior – AI can provide customized infotainment during travel. Based on the data collected over time, AI can predict and prescribe preferences based on user behavior. This could include:
- Seat position adjustment
- Mirror adjustment
- Regulating the air-conditioning
- Songs to be played
AI is gaining in prominence with each passing day and urges people to experience the ease of riding in an effortless autonomous car. Governments too have jumped into the race to woo investors to bring AI-based driverless cars to commercial use.
In August 2018, the British Government unveiled plans for an AI simulator intended for the purpose of attracting companies as a favorable destination for testing self-driving cars. Named as OmniCAV, the simulator can recreate a virtual version of 32km of Oxfordshire roads.
The world is changing faster than imagined, and AI is getting smarter with every passing day. We're just around the corner to witness the post-Uber era, so hold your breath tight!
Written by Rilind Eleza
The Most Comprehensive IoT Newsletter for Enterprises
Showcasing the highest-quality content, resources, news, and insights from the world of the Internet of Things. Subscribe to remain informed and up-to-date.
New Podcast Episode

Navigating the Future of Embedded Computing
Related Articles