Bluetooth Will Revolutionize Industrial IoT
Bluetooth Will Revolutionize Industrial IoT
- Last Updated: December 2, 2024
Guest Writer
- Last Updated: December 2, 2024



There are only a handful of wireless connectivity options, and each one has its pros and cons. There's mobile — including 3G, 4G and the upcoming 5G — Wi-Fi and Bluetooth. Low-power wide-area networks (LPWANs), satellite communications and RFID are some additional options.
In industrial and enterprise settings, Wi-Fi has been the crowning champion for some time. It’s cost-effective, offers great performance, and can be easily extended across large properties or facilities with the help of mesh network systems. Mobile connectivity, on the other hand, is much more expensive. While still lucrative, it's most viable for on-the-go situations — such as syncing up a transport fleet.
Bluetooth has been relegated to the consumer market, commonly used in applications such as mobile to smart device connectivity, wireless audio and similar functions. Most portable and smart speakers, for instance, have Bluetooth built-in and allow users to sync their device to play music and media remotely.
Bluetooth tends to come with more limitations than the other connectivity options, particularly when it comes to the technology’s effective range.
More recently, however, we’re seeing that start to change. Thanks to advancements with the technology (Bluetooth mesh networks) and growing awareness as part of the Bluetooth SIG’s efforts, it’s looking more lucrative than ever on the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) front.
What Makes Bluetooth Ideal for IIoT Applications?
Many of the inherent limitations with Bluetooth manifest only in consumer applications, and most importantly, in older versions of the technology.
Bluetooth wireless connectivity isn't known for having a long range, for instance, with most believing the maximum supported distance is several meters at best.
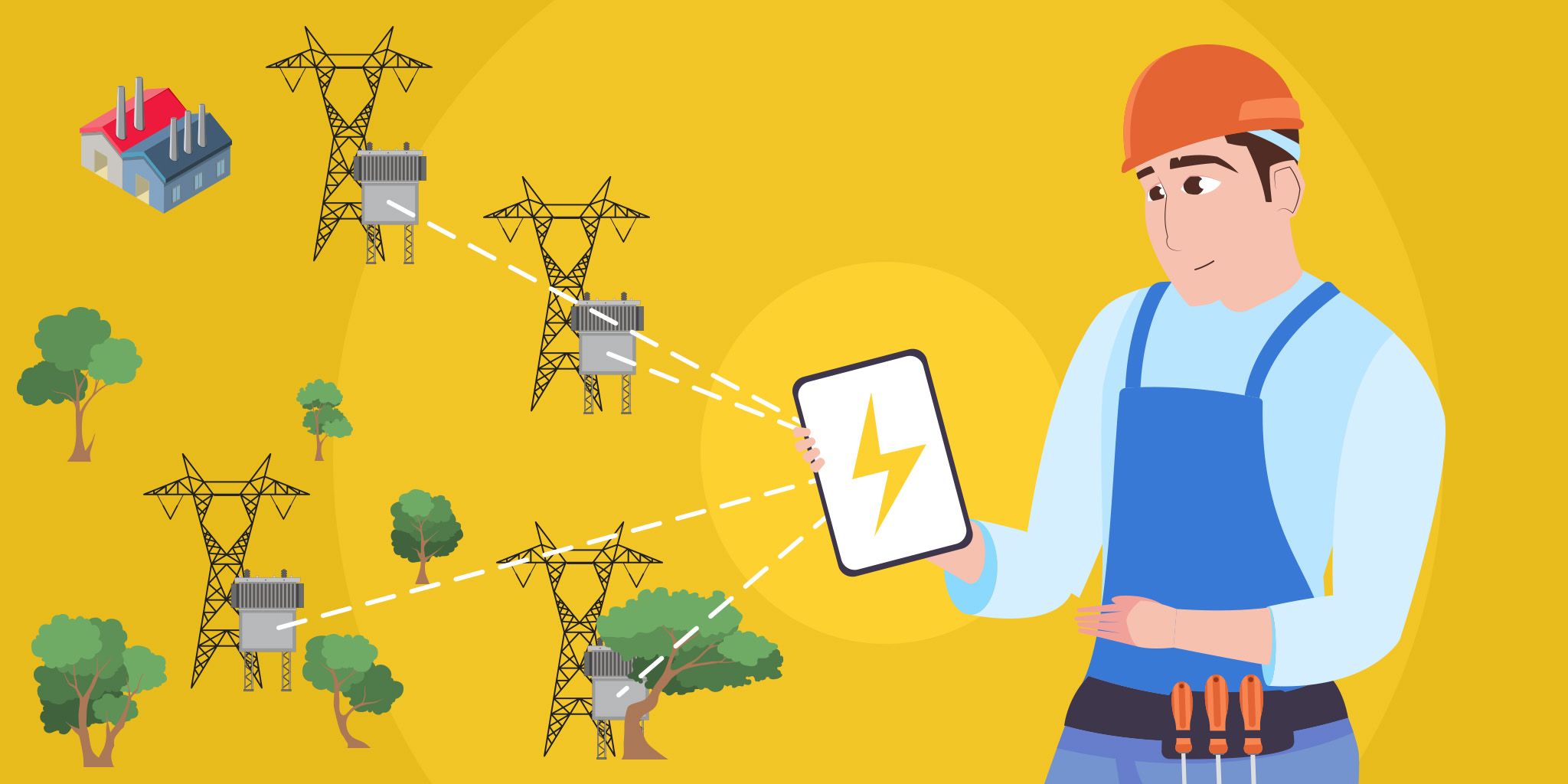
In reality, Bluetooth can operate over much greater distances and performs well even in harsh conditions — many of which exist in industrial environments. The latest standard, Bluetooth 5.0, supports a long-range mode that can be used to transmit messages up to 1.7 km (1.05 miles) away.
Bluetooth is an exceptional technology choice for more than just the extent of its range. It's also highly immune to interference, something that Wi-Fi commonly struggles with, especially across large properties.
There’s almost no limit to the number of devices you can have connected and the amount of data transmitted via the standard. It’s an extremely secure connection thanks to its inherent traits.
Bluetooth is also a relatively low-power system, which can help maintain lower operations costs. This is especially helpful when there are dozens, if not hundreds, of on-property machines using the technology.
It can be incorporated quite easily with existing equipment, as well. There’s no need to upgrade, revise or swap things out in many cases, either. Serial ports are often used in industrial applications, and Bluetooth is compatible with such hardware thanks to its serial port profile (SPP).
Finally, and this is perhaps one of the most important, it can detect and rectify bit errors via the receiver. This means that incorrect data can be avoided thanks to something called forward error correction, or FEC. This is incredibly important in industrial spaces where real-time measurements must be precise.
Bluetooth offers a reliable, scalable and low-cost IIoT solution thanks to mesh networking, low resource usage, many-to-many applications, fast speed and a long operational range.
Bluetooth Mesh Networks
Aside from the long list of features and the rollout of Bluetooth 5.0 — the latest and most capable version of the standard — the introduction of mesh applications has truly augmented the technology’s potential in the industrial field.
Launched in July 2017, Bluetooth Mesh amplified the usual one-to-one connections that most devices shared to incorporate many-to-many (m:m) device communications.
This means that, just like conventional mesh networks, Bluetooth Mesh opens up the technology and its proponents to widespread communication on a larger scale. Bluetooth can be used to sustain high-capacity systems, exactly the type needed to power smart buildings and smart industry applications. It allows tens, hundreds or thousands of devices to communicate with one another effectively.
Chuck Sabin, the senior director of market development for the Bluetooth SIG, says that “Bluetooth mesh networks are ideally suited for control, monitoring and automation systems.” He goes on to say that the technology offers low-latency support and unprecedented security for such applications, as well.
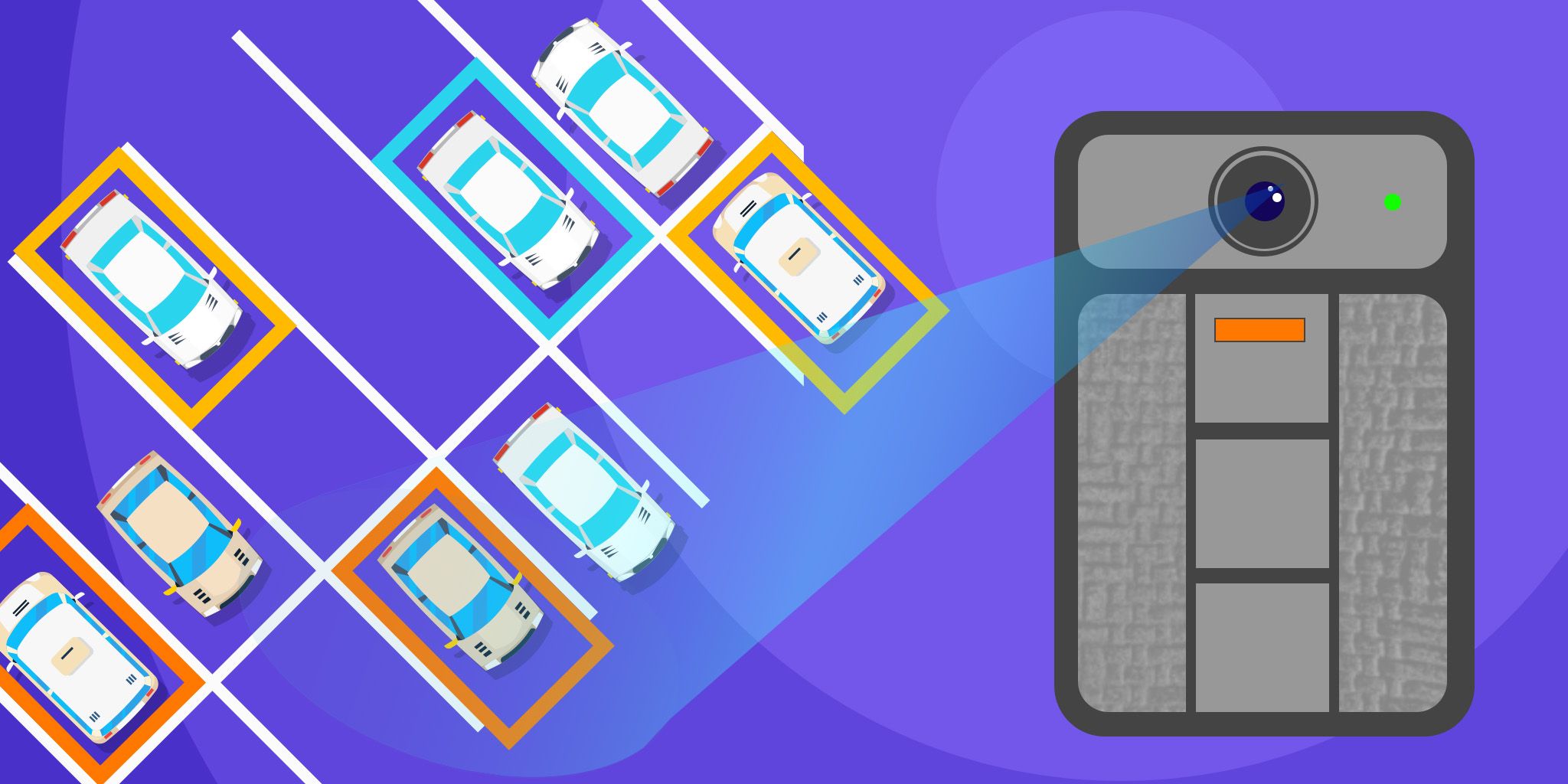
On top of that, Bluetooth SIG also announced a new direction-finding function for the technology that further improves its location-services support. By identifying the direction of a Bluetooth signal and comparing it to known information, it offers “centimeter-level” precision for location-based applications.
The technology can be effectively used for low-cost yet incredibly accurate indoor location and asset tracking solutions. Imagine being able to identify which room or storage area a tool is located within the walls of a sweeping compound?
All these things have culminated in the perfect storm that’s driving up the adoption of Bluetooth in industrial fields, and for good reason.
Bluetooth SIG recently predicted a sevenfold growth in annual shipments of Bluetooth smart-building location services devices by 2023. A five-times growth is also predicted for yearly shipments of Bluetooth smart-industry devices by 2023, alongside a three-and-a-half times growth in the increase of Bluetooth enterprise wearables shipments by 2023.
What’s Next for Bluetooth in IIoT?
The biggest hurdles IIoT and Bluetooth will face when it comes to widespread adoption are the misconceptions surrounding the technology. Thankfully, these have begun to shed in recent years.
The latest standard has massively boosted the operation range, increased speeds, introduced mesh networking or many-to-many applications and decreased resource usage. It’s possible to run a Bluetooth LE device on a coin-cell battery for months or years at a time.
All of this, coupled with the reliable security and scalability of its wireless communication, makes Bluetooth a remarkably ideal solution for industrial organizations.
As for how the technology is going to revolutionize the IIoT market, it’s going to kickstart adoption specifically among players that had no vested interest in the past. It’s hard to deny the convenience and value of IoT in today’s ever-digital and hyper-fast market.
Bluetooth will offer a reliable, scalable and low-cost solution for augmenting entire plants and facilities. We’re talking about the smart buildings and factories of the future that will rely on this tech to grow and move forward.
Written by Caleb Danziger
The Most Comprehensive IoT Newsletter for Enterprises
Showcasing the highest-quality content, resources, news, and insights from the world of the Internet of Things. Subscribe to remain informed and up-to-date.
New Podcast Episode

Navigating the Future of Embedded Computing
Related Articles