Finding Value In Industrial Data with AI
Finding Value In Industrial Data with AI
- Last Updated: December 2, 2024
VROC
- Last Updated: December 2, 2024



All industries have one thing in common, data and lots of it. The amount of data is related to the volume of ‘things’ now connected to the internet, from personal devices, the office printer, all the way to the sensor on a pump that is helping generate the electricity necessary to keep the power on.
They say data is the new oil; however, far too many industrial companies are finding little to no use or benefit from all the data they are generating. In fact, the Mining and Resources sector is reported to use less than 1 percent of the data collected from their equipment.
So how do companies ensure they are getting the most value from the data generated, and how do we ensure that the project is a success and doesn’t become another statistic in the 70 percent of all digital transformations that fail?
These questions can be solved by looking at who in your organization uses data and what data is analyzed.
Data Science Approach
Before Industry 4.0, it was uncommon for industrial businesses to rely on their data for everyday decision-making. Businesses relied on time-proven methods, such as preventative maintenance, just-in-time maintenance, the implementation of OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) specifications, and the practice of bringing in external SMEs and consultants as required to help resolve reliability issues and optimize processes.
Once a company discovers the value of its data and begins to utilize data insights across the organization, true digital transformation is possible.
With the introduction of Industry 4.0, and as IoT sensors have become more commonplace, businesses have begun to collect their data. Many large organizations created internal data science teams to use the newly acquired data to work on critical issues.
Typically, these issues would be solved by looking at limited historical data. The data science team would spend an enormous amount of time on repetitive data manipulation tasks, programming, and coding. With this process, data insights often take months to generate.
This approach restricts the analysis of the data to the data science team. Yes, these businesses are putting their data to use; however, scaling results is difficult due to the time required to generate insights. Unfortunately, over the last few years, many of these data science teams have been downsized, as the business value hasn’t been recognized.
No-Code AI Approach
A term called ‘data democratization’ occurs when individuals throughout an organization start using data in their everyday positions. These people are not statisticians, mathematicians, data engineers, or data scientists. In fact, they are not interested in data at all; they are only interested in what the data can tell them.
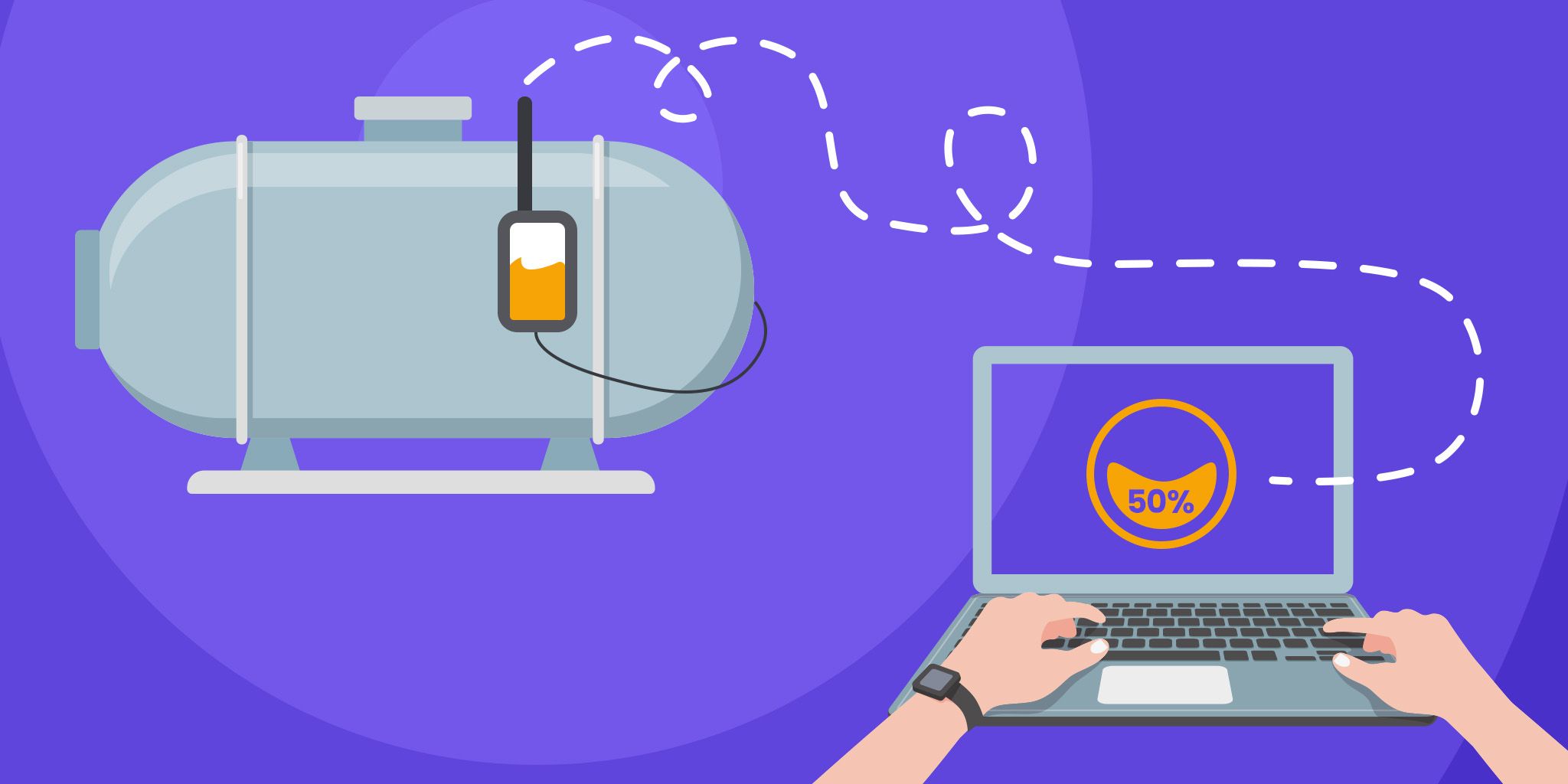
Technology has advanced, and do-it-yourself no-code AI platforms now allow asset managers, maintenance personnel, operations teams, and engineers to learn from their data and obtain insights to help their everyday decisions.
Some examples of the types of decisions no-code AI assists are:
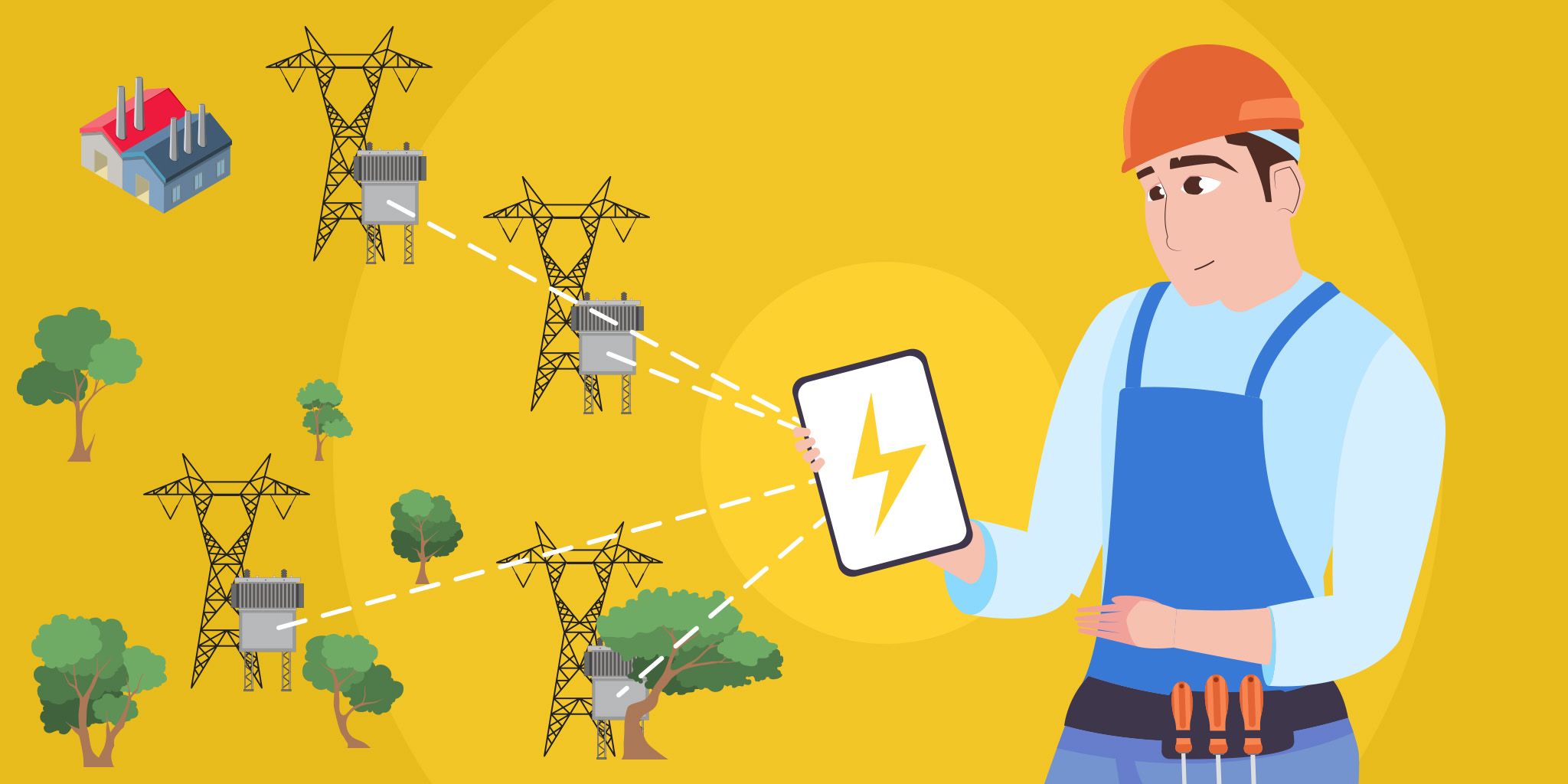
- Live monitoring of assets and industrial processes so teams know where to focus their efforts
- Predicting future failures of equipment for early intervention
- Optimizing fuel consumption for a power plant by identifying a fault in an air supply system
- Reducing OPEX in late life industrial assets
- Accurately identifying the root cause of a potential contamination incident, avoiding a significant safety event and improving environmental outcomes
- Establish Co2 emission baselines and help provide insights to reduce energy consumption
- Understand the correlation between different systems and processes, and avoid instability and damage, such as in the case of sand production between the subsurface and top-side of an oil and gas platform
- Provide real time set points for accurate chemical dosing at a water treatment plant
No-code Artificial intelligence gives non-data-focused roles insights to help them make more informed decisions throughout the day. Users can build models of their equipment and processes to provide calculated predictions and insights. Data democratization occurs when SME’s, end-users, and operators can extrapolate critical insights without programming, coding, calculating, or even opening an excel spreadsheet.
Data Analysis: Single Asset vs Holistic
Typically, organizations work in silos, operations and optimization are separate departments, and data is not shared across departments. In some organizations, data is not even shared between different units in the one department – think operations subsea and operations topside on an oil rig.
To make matters even worse, the method by which data has typically been analyzed is quite limited. For example, if there is a problem with the compressor, we will only analyze historical data from the compressor. This approach does not always guarantee an accurate result, as the root cause of the problem may not exist in the compressor itself.
A holistic approach to using data (both live and historical) to analyze a problem ensures that nothing is missed. No-code artificial intelligence finds correlations in data that manually may take months to find - and that’s if you are analyzing the right data set from the beginning. Some correlations that AI can detect are from seemingly not interconnected processes at all, and the traditional approach won’t identify.
The Head of an Offshore Operation remarked, ‘Technically you couldn’t get this particular decision to be made as fast as that’ when talking about the root cause of a problem being identified from a separate process that was not inter-related. No-code artificial intelligence can, within minutes, analyze years of data and provide critical insights or predictions to help teams make improved business decisions.
Condition monitoring, which typically only triggers alarms once thresholds are met, can be bolstered by artificial intelligence to detect minor degradation, giving more time for planning. The live models which continually refresh can monitor whole facilities and operations. Giving a holistic view of performance, identifying risks and opportunities to help businesses get ahead.
Combining Who and What
As a business works smarter and learns from all available data, efficiencies and decisions improve across the organization. By democratizing data and equipping personnel (the who) to get insights from data that they can implement on the job immediately (the what), the speed to produce value from that data increases.
Once a company discovers the value of its data and begins to utilize data insights across the organization, true digital transformation is possible.
The Most Comprehensive IoT Newsletter for Enterprises
Showcasing the highest-quality content, resources, news, and insights from the world of the Internet of Things. Subscribe to remain informed and up-to-date.
New Podcast Episode

Navigating the Future of Embedded Computing
Related Articles