IoT to Enable Smart Environmental Monitoring
IoT to Enable Smart Environmental Monitoring
- Last Updated: December 2, 2024
Semtech
- Last Updated: December 2, 2024



Sustainability and the protection of the environment are without a doubt among the most pressing issues we face in the world today. As more people start to understand the need to sustainably manage the planet’s resources and ecosystems, more organizations are focusing on smart environmental monitoring technology to create a more connected and sustainable planet. According to the World Economic Forum report on IoT Guidelines for Sustainability, 84 percent of IoT deployments are currently addressing, or have the potential to address, the Sustainable Development Goals defined by the United Nations. IoT, then, has revolutionized the way we connect and interact with devices designed for social and environmental good.
'IoT has the power to serve as a building block of smart environmental monitoring by maximizing efficiencies, reducing waste, and better managing our precious natural resources.' -SemtechCorp
With a network of sensors and gateways embedded with long range, low power technology across regions, organizations can implement environmental indicators that measure, provide data analysis, and detect issues in real time. This type of network makes it possible to have sensors/devices collecting and sending data at a lower cost, over a longer range, and with significantly extended battery life.
From animal conservation to flood detection, IoT helps protect people from environmental dangers. Here are just a few examples of how organizations can implement smart environmental monitoring.
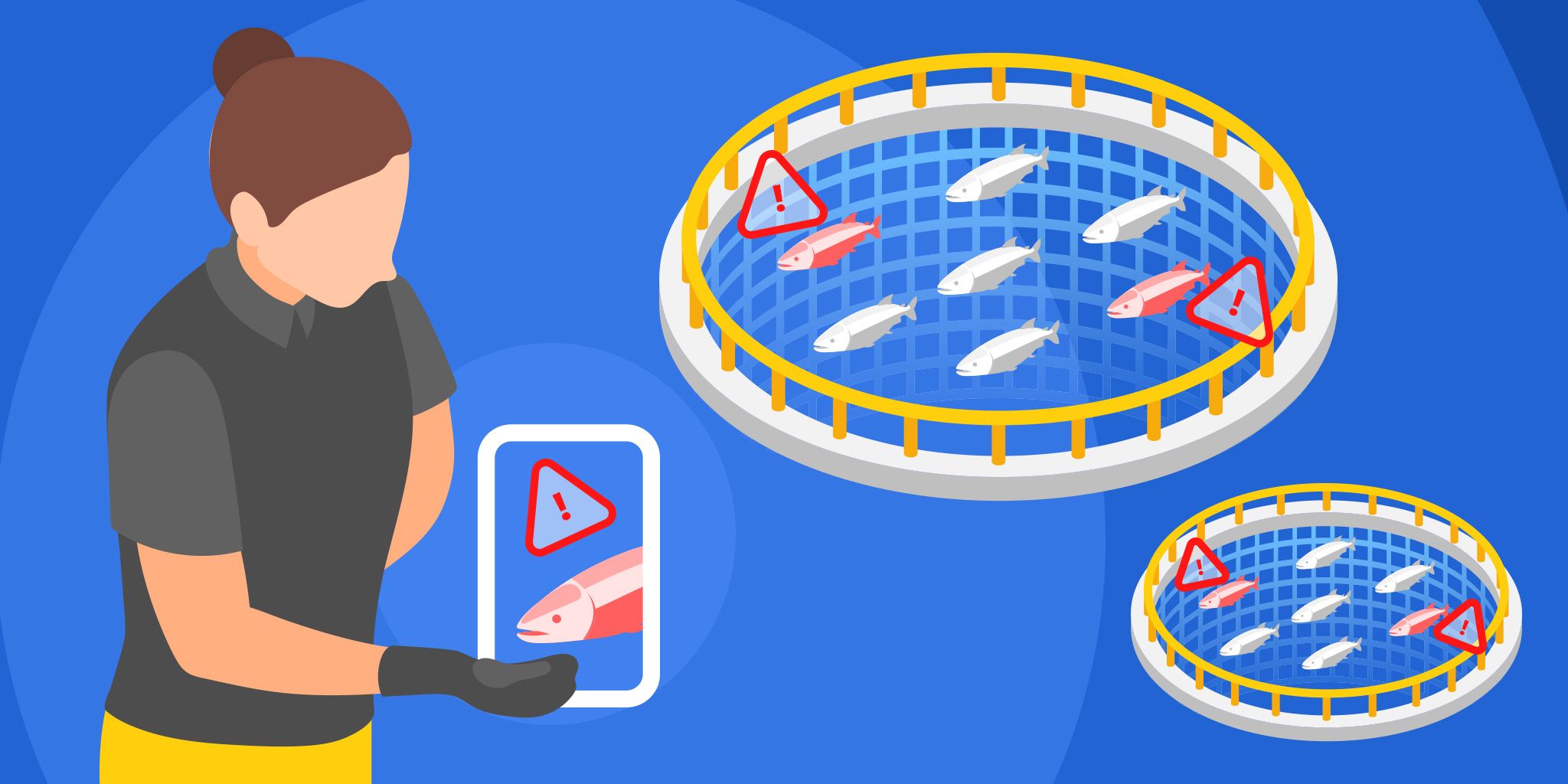
- Water Conservation: According to the United States Environmental Protection Agency, household leaks waste approximately nearly 900 billion gallons of water annually nationwide. By integrating sensors into water management systems, smart homes and buildings can efficiently monitor their water usage, detect leaks, and decrease water wastage.
- Animal Conservation: Most national parks protecting endangered species lack connectivity. Without a way to intelligently track the animals and their movements, it is difficult for rangers to monitor national parks. IoT solutions with a reliable network help create a sustainable and safe way to track animals simply and efficiently. These networks serve to collect data from sensors distributed throughout expansive areas.
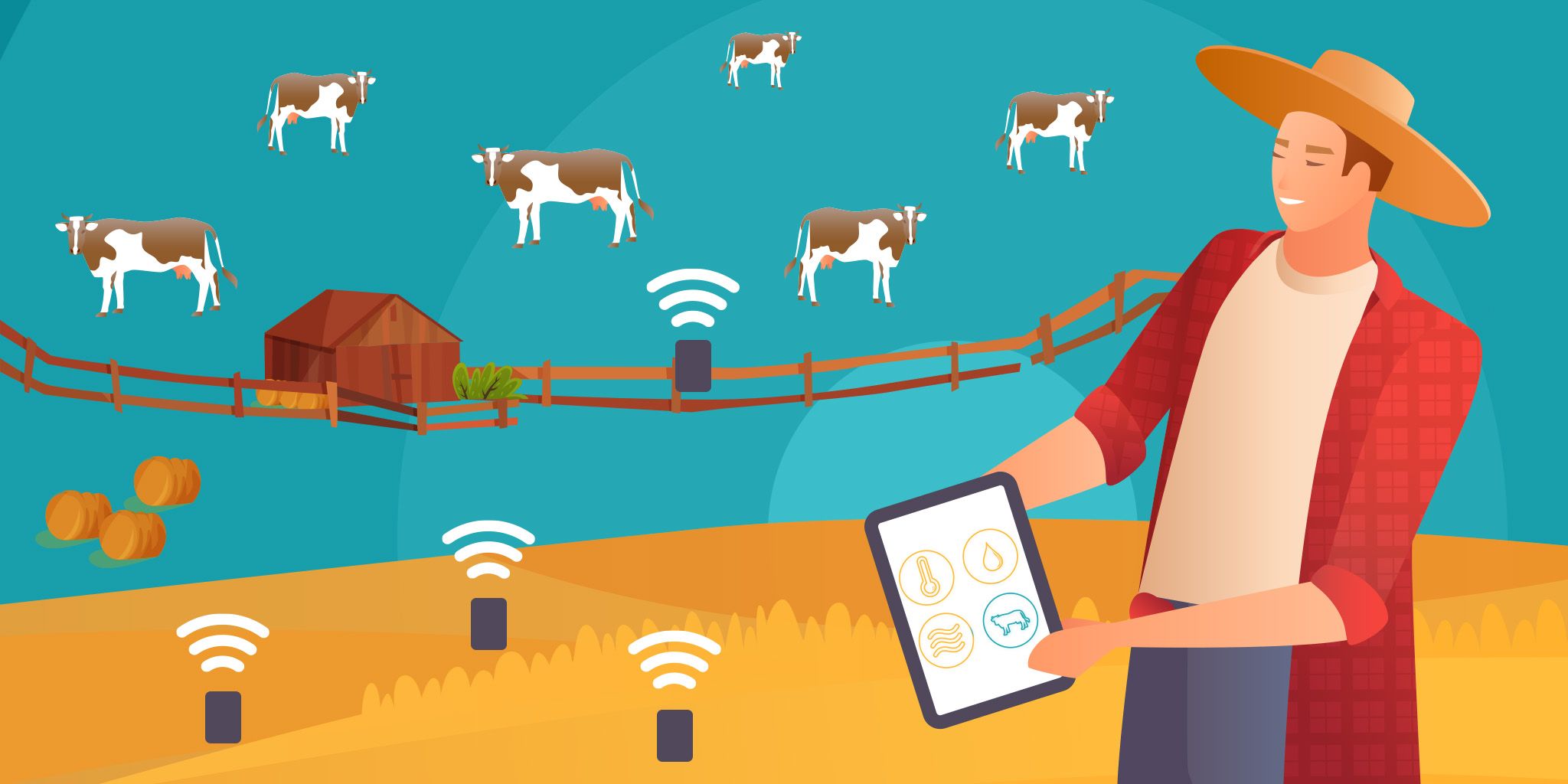
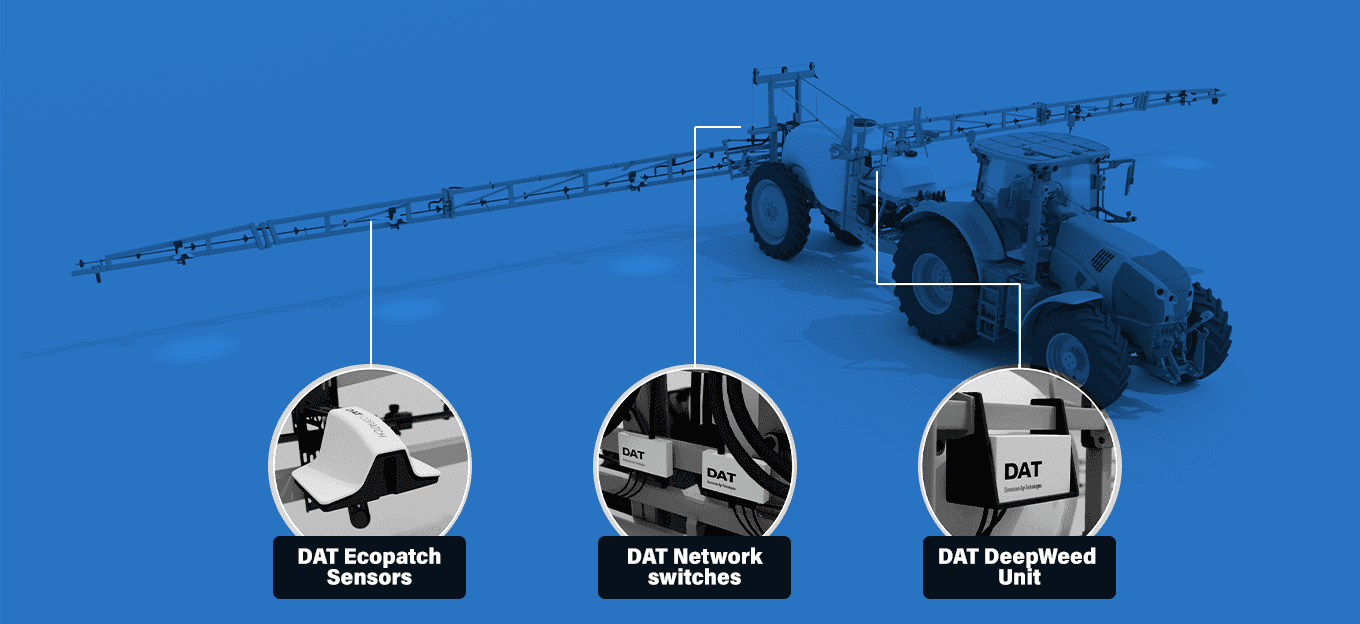
- Sustainable Farming: IoT technology is bringing the physical world of farming into the future. Whether that means using sensors to track soil conditions, water levels, or the quality of their crops, farmers are greatly benefiting from connectivity. Long-range, low-power sensors can measure environmental conditions that influence crop production, track the health of livestock, and enable efficiencies that can reduce environmental impact while maximizing yield and minimizing expenses.
- Flood Monitoring: To respond faster to floods and prepare for future ones, governments need to monitor waterways in real-time, predict the risk of flooding, and alert emergency personnel and citizens in advance of a flooding event. Sensors integrated with long-range, low power technology autonomously monitor rising sea levels as a result of climate change. The use of these sensors has been valuable in coastal regions with a high risk of flooding.
As climate change initiatives come to the forefront for organizations, IoT has the power to serve as a building block of smart environmental monitoring by maximizing efficiencies, reducing waste, and better managing our precious natural resources.
The Most Comprehensive IoT Newsletter for Enterprises
Showcasing the highest-quality content, resources, news, and insights from the world of the Internet of Things. Subscribe to remain informed and up-to-date.
New Podcast Episode

Navigating the Future of Embedded Computing
Related Articles