The Role of IoT In EMR & Clinic Management
The Role of IoT In EMR & Clinic Management
- Last Updated: December 2, 2024
Alexandr Khomich
- Last Updated: December 2, 2024



More people are using IoT devices today than ever before. According to Statista, the number of connected devices will triple from 8.74 billion items in 2020 to 25.4 billion in 2030. The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) will constitute a significant part of them. The value of the medical market will quadruple to over $260 billion. The reason for such rapid growth is that connected devices are becoming faithful assistants to doctors and are used in medical practice and hospital management. Let’s consider the benefits of IoT for EMR and clinic management software.
'IoT in EMR and clinic management software will enrich old platforms with new functionality.' - Andersen
Why IoT?
To make diagnoses, treat patients, conduct research, or invent new medicines, doctors need to collect and analyze a lot of information. In 2020 alone, the industry generated up to 2,314 exabytes of new data, which is 15 times more than in 2013. Physicians need to choose valuable medical information out of the flow of unstructured data. IoT devices and sensors help to solve this problem.
An electronic medical record (EMR) is more than a digital version of a paper medical record. Such software stores important patient data (medical history, chronic diseases, immunization dates, allergies, doctor’s records, etc.). Doctors make fewer mistakes in electronic documents than in handwritten records, and some manual tasks are automated. If you connect an EMR with IoT devices and sensors, you’ll obtain a great tool for remote patient monitoring.
Hospital management software plays an important role in a healthcare facility. It includes tools for monitoring medical, administrative, financial, and legal issues. The program helps to plan the working schedule of the staff, control compliance with regulatory requirements, and manage inventory and medical equipment. IoT sensors may become the “eyes and ears” of the hospital administration as they help to monitor the hospital workflow.
Benefits of IoT for EMR and Clinic Management Software
Let’s take a look at three specific ways IoT improves EMR and clinic management software. These two programs function together, which makes it necessary to consider IoT perspectives for them both.
#1: Remote Patient Monitoring
According to Statista, by 2030, the revenue from remote IoT monitoring will almost double and reach $2 billion. IoT sensors and devices capture a patient’s vital signs and other important rates. These includes:
- Heart Rate
- Oxygen Saturation
- Arterial Pressure
- Blood Sugar Level
- Sleep Statistics
- Body Temperature
Connected devices are integrated with EHR/EMR and transmit the data to the system. A doctor assesses the information and adjusts the treatment according to these parameters. When the program captures critical health rates, it sends an alert to hospital nurses. IoT sensors can be installed both in the patient’s house and in a hospital department. With their help, doctors and nurses provide patients with personalized treatment, regardless of their location. This is a critical asset for EMR and clinic management, as patients do not always have to come in to receive treatment.
#2: Medication Tracking
Smartphones, smartwatches, and IoT sensors are used to manage medicines in the hospital and at home in the following ways:
- Tracking the Origin of Medicine: Sensors attach to boxes with medicine record information. The hospital administration checks where the medicines have come from and whether they are damaged or not.
- Monitoring Medication Intake: A smartphone can be used to install a reminder application. A patient sets up a schedule for taking medications, and push notifications are sent to their smartphone at the right time. The patient does not neglect the treatment and recovers faster.
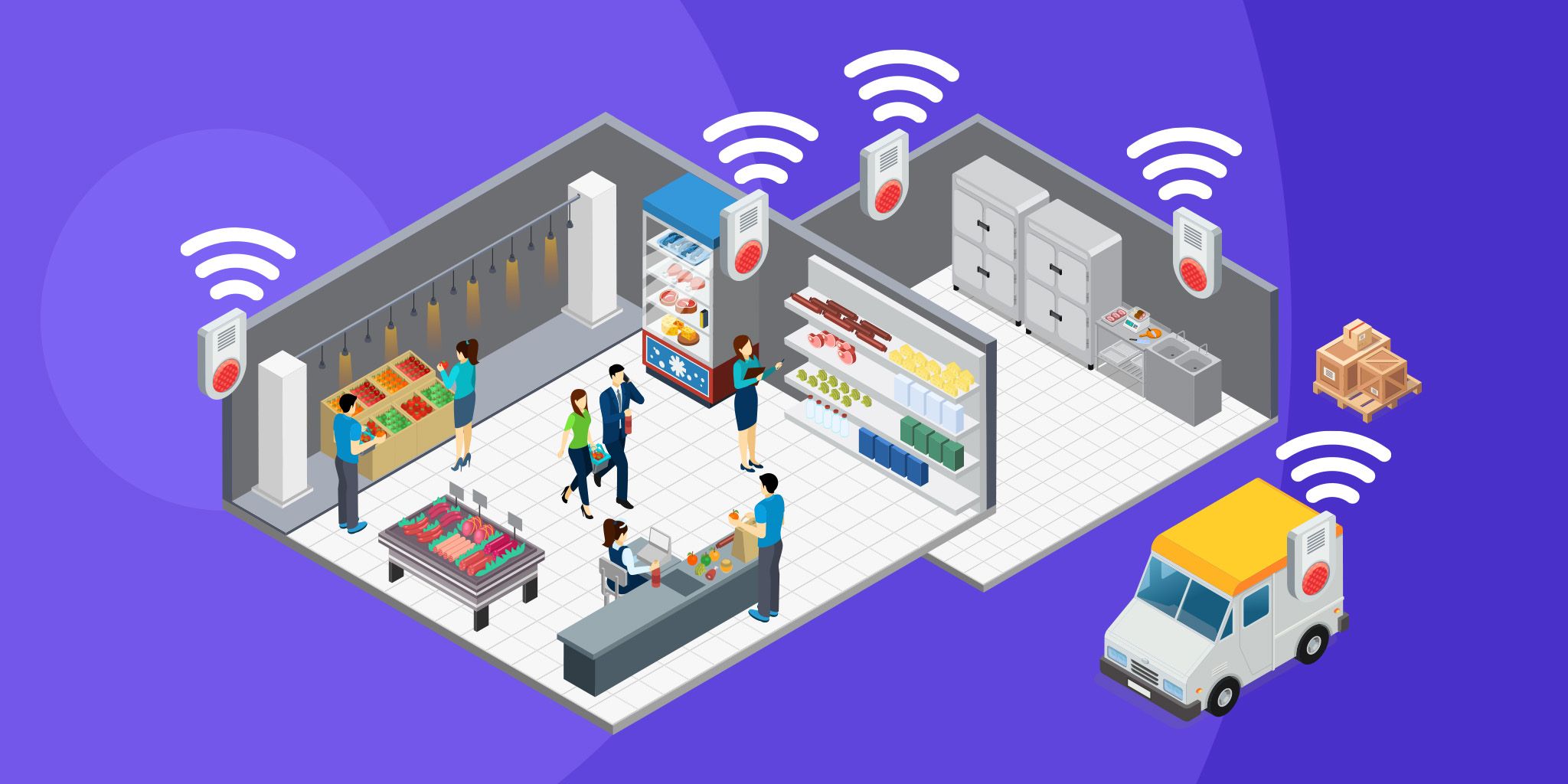
#3: Tracking Valuable Medical Equipment
Every year, up to 25 percent of wheelchairs are lost in the US. There are thousands of hospital devices and items that you must be able to find on-demand. A real-time IoT location system (RTLS) can help to perform a search.
The system includes IoT readers and tags. An RFID tag is attached to each item that has a unique number registered in the inventory software. The hospital possesses IoT readers that receive RFID signals and transmit data to the interface part of the system. A doctor’s smartphone or computer receives the information on which floor and in which office the required device is located. This “search engine” is useful when the staff needs to make an inventory or urgently find an oxygen mask for a newly admitted critical patient.
IoT Use Case Example
An American healthcare facility built a new EHR system with IoT functionality. For that purpose, it contacted a healthcare software development company. The IT partner received the task of creating a tool that would improve communication between different branches of the organization and help to carry out remote patient monitoring.
The developers created an electronic medical record with embedded IoT functionality (smartwatches, trackers, wireless ECGs, blood pressure monitors, and sensors for tracking the patient’s location). The app displays the screen of a patient’s record and IoT sensors capture important health data and transmit it to a nurse for control. When the rates deviate from the norm, the app sends an alarm, and the nurse contacts the patient to schedule a consultation with a doctor.
The doctor conducts a teleconsultation and prescribes treatment based on the patient’s medical history. The EHR is integrated with the hospital inventory management system and hospital management software. With the help of an IoT-based EHR solution, the healthcare facility managed to reduce hospital admissions by 20 percent and increase revenue by 11 percent.
Integrating IoT
IoT in EMR and clinic management software will enrich old platforms with new functionality. It will allow for the remote treatment of patients and help the administration to control numerous processes, from checking the quality of medicines to inventory management.
If your clinic needs to add the IoT functionality to EMR and hospital management software or create a new IoT solution, you should contact a healthcare software development company. Choose an IT partner based on their experience in implementing similar projects, technical skills, and expertise in HIPAA and GDPR.
The Most Comprehensive IoT Newsletter for Enterprises
Showcasing the highest-quality content, resources, news, and insights from the world of the Internet of Things. Subscribe to remain informed and up-to-date.
New Podcast Episode

Navigating the Future of Embedded Computing
Related Articles