Why We Need Predictive Maintenance in Industry 4.0
Why We Need Predictive Maintenance in Industry 4.0
- Last Updated: December 2, 2024
Guest Writer
- Last Updated: December 2, 2024



Maintenance and Repair Operations (MRO) are vital for the proper functioning of enterprise assets while being key to business operations' continuity and effectiveness. MRO involves a wide range of activities, including:
- inspecting industrial installations
- performing functional checks on devices and equipment
- replacing damaged or malfunctioning parts
- repairing machinery
- performing various field service engineering tasks.
The planning and execution of these activities require significant human resources and represent a considerable line in industrial organizations' budgets. This is why enterprises are constantly seeking ways to improve the efficiency and cost of their maintenance activities.
Predictive maintenance can assist enterprises in improving the efficiency and cost of their maintenance activities.
This article will go over the difference between preventive and predictive maintenance and go over business cases for predictive maintenance strategy.
Preventive Maintenance vs Predictive Maintenance
In the past, enterprises maintained their assets reactively. Business repaired or replaced an asset after it had broken down. Accordingly, the asset was restored to its original condition. Reactive maintenance was problematic because it is associated with equipment breakdowns, which stop activities and lead to huge losses.
To mitigate the inefficiencies of reactive maintenance, industrial organizations transitioned to the preventive maintenance model. Preventive maintenance schedules repair and service operations at regular intervals to prevent equipment failures. In other words, preventive maintenance considers the assets' expected lifetime to inspect and maintain them proactively. In this way, it alleviates unexpected downtime and boosts the continuity of business operations.
What Is Predictive Maintenance Strategy?
Preventive maintenance is currently the dominant enterprise maintenance approach. Nevertheless, it is far from optimal, as it typically maintains assets earlier than their end of life (EOL). Hence, it leads to a sub-optimal Overall Equipment Efficiency (OEE). To achieve optimal OEE, enterprises must plan maintenance activities based on factual information about the assets' status rather than based on hypothetical EoL values.
This is where predictive maintenance comes in. Predictive maintenance means businesses can schedule maintenance activities based on accurate predictions about an asset’s lifetime.
Predictive maintenance offers many business benefits when compared to the conventional reactive and preventive models:
- Improved Asset Utilization and OEE: With predictive maintenance, enterprises make the best possible use of their assets and improve their OEE.
- Avoidance of Unscheduled Downtimes: Predictive maintenance provides visibility on the actual condition of the assets, which minimizes possible unscheduled downtimes.
- Optimal Planning of Maintenance Activities: Information about the asset’s conditions and their anticipated EoL can be combined with insights on business operations (e.g., production schedules, demand forecasts) towards maximizing revenues and minimizing MRO costs.
Predictive Maintenance: An Industry 4.0 Application
The benefits of predictive maintenance translate to significant cost savings and increased revenue for business enterprises that manage large installations. Nevertheless, predictive maintenance is still not widely deployed, given that getting access to timely and detailed information about the assets’ condition is quite challenging.
In recent years, this is gradually changing thanks to the proliferating deployment of sensing systems and advanced digital technologies (e.g., Internet of Things, BigData, Artificial Intelligence) in large organizations' production facilities. The deployment of these technologies form parts of the so-called fourth industrial revolution (Industry 4.0).
Industry 4.0 is about deploying sensors and cyber-physical systems to digitize physical processes and implement IT-based data-driven automation and control operations. Industry 4.0 enables a rich set of industrial applications such as flexible automation, predictive maintenance, digital twins, and various supply chain management optimizations.
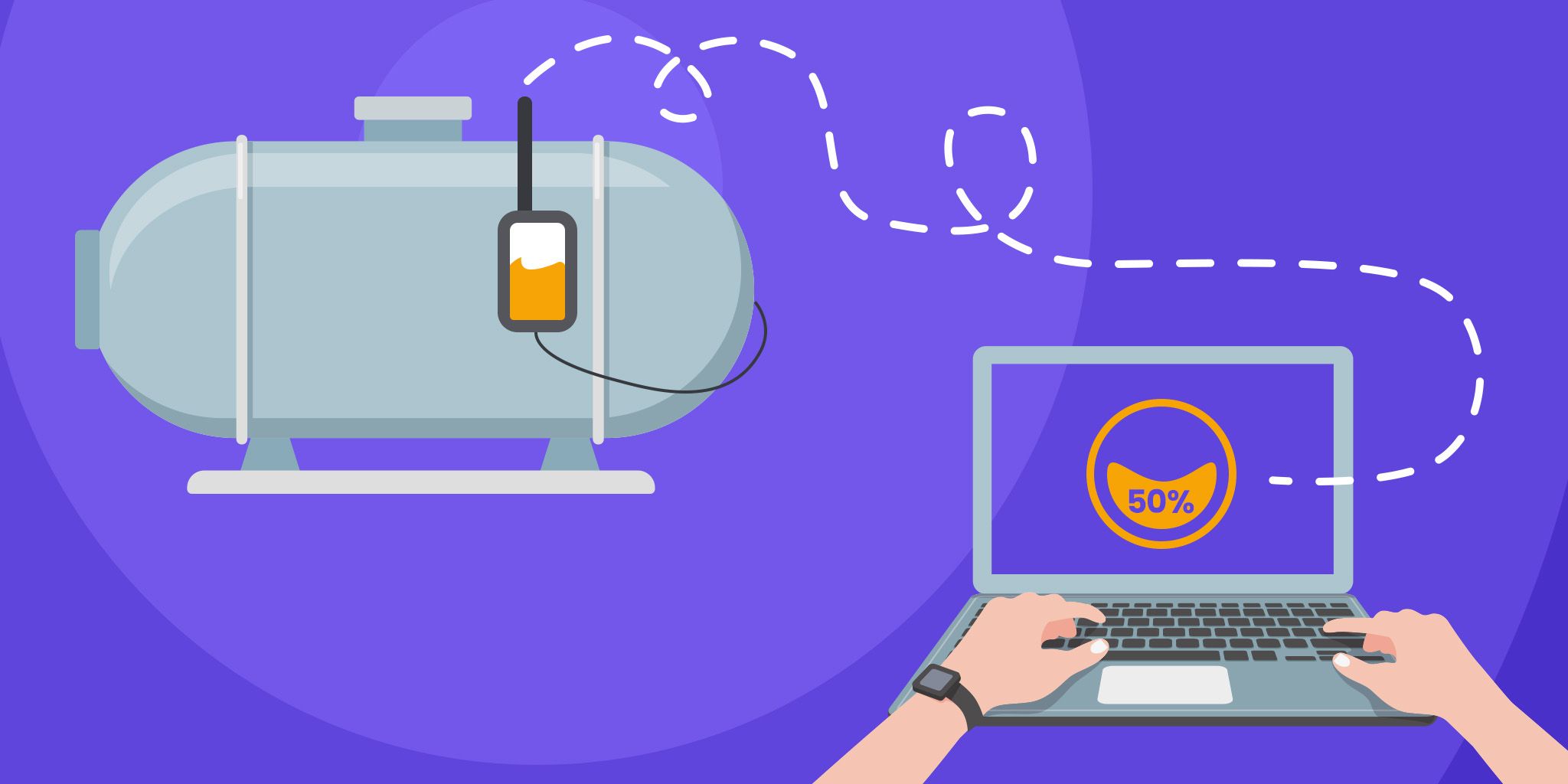
In the area of enterprise maintenance, Industry 4.0 facilitates the collection of large volumes of digital data about the condition of machinery and equipment. This data collection is empowered by deploying different types of sensors, like vibration sensors, acoustic sensors, temperature sensors, power consumption sensors, and thermal cameras.
Predictive Maintenance Strategy
Overall, predictive maintenance applications are empowered by modern networks of sensors, which collect large amounts of data about asset conditions. Industrial organizations deploy complex sensor data collection infrastructures consisting of wired or wireless sensors. These infrastructures can cope with the different rates and formats of the data streams of the various sensors.
In most cases, data from sensor networks are usually persisted and managed within scalable cloud computing infrastructures. The latter enables the deployment of Big Data infrastructures to handle huge volumes of heterogeneous datasets, including data with very high ingestion rates.
The availability of rich sets of digital data for the assets' condition provides a sound basis for determining key maintenance parameters such as an asset’s Remaining Useful Life (RUL). Maintenance datasets are processed by modern Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence techniques such as Deep Learning. This leads to the extraction of insights about asset conditions and the parameter calculations like EOL and RUL.
Predictive Maintenance Tools & Techniques
Insights about the assets’ conditions are usually visualized in dashboards and presented to maintenance personnel like maintenance engineers and technicians. A typical visualization solution for predictive maintenance presents information about each asset's health and condition, including information that instructs maintenance professionals on how to best schedule maintenance activities.
In practice, maintenance engineers and service technicians use the information visualized in dashboards as part of their maintenance planning and decision-making methodologies, like:
- Reliability Centered Maintenance (RCM).
Predictive Maintenance Applications
Asset health information can be leveraged by IT-enabled predictive maintenance applications to enable a range of intelligent applications such as:
- Intelligent Control for Optimizing Asset Utilization
- Maintenance Schedules Optimization
- Simulating the Future Condition of the Asset
- Root Cause Analysis
- Leveraging Augmented Reality for Remote Maintenance:
Intelligent Control for Optimizing Asset Utilization
Maintenance insights can be used to drive automation and control functions to optimize asset utilization. For example, upon detecting early signs of asset degradation, a different operational mode can be activated to avoid stopping operations and prolonging the asset’s Remaining Useful Life (RUL).
Maintenance Schedules Optimization
This application combines maintenance information about individual assets (e.g., a machinery’s RUL) with insights about business processes (e.g., production schedules, customer orders) towards producing optimized maintenance schedules. These schedules indicate the best point to perform asset maintenance, considering how to maximize OEE and the utilization of the asset and how to maximize revenue.
Simulating the Future Condition of the Asset
Predictive maintenance parameters can be integrated with powerful digital twins applications to simulate the asset’s future behavior. Likewise, what-if scenarios regarding asset maintenance and operation can be simulated. These simulations can help maintenance professionals evaluate alternative maintenance options and their impact on business operations.
Root Cause Analysis
It is possible to track the health status of assets over time to identify possible causes of their performance degradation. The identification of such causes helps enterprises improve the ways they use and maintain their assets. Artificial Intelligence (AI) algorithms can identify hidden patterns of degradation beyond existing domain knowledge in several cases. This discovers the root causes of failures and identifies proper remedial actions.
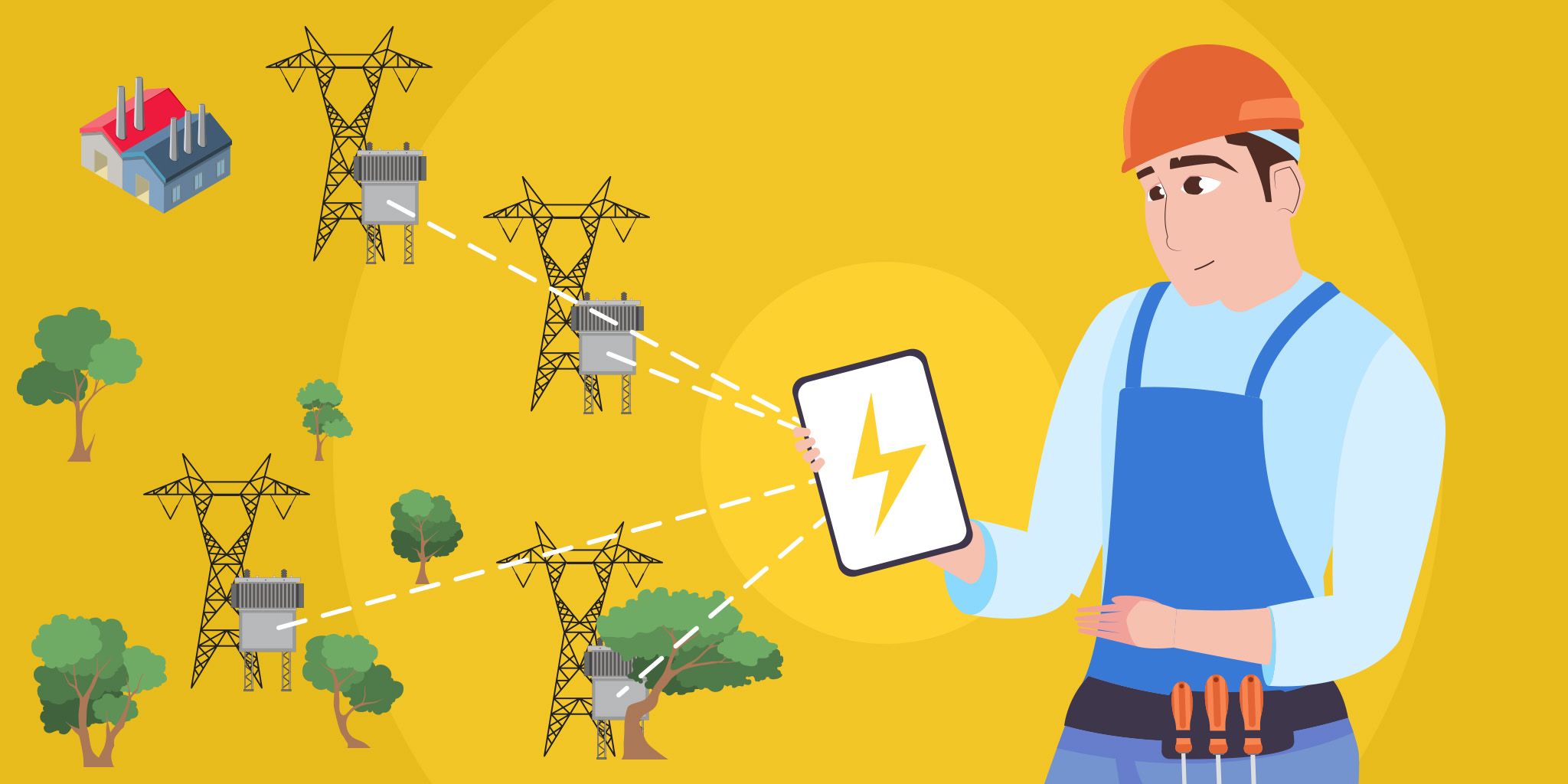
Leveraging Augmented Reality for Remote Maintenance
The extraction of predictive maintenance insights on assets can also give rise to remote maintenance processes. Augmented Reality visualizations are used to indicate to technicians how to maintain specific assets (e.g., repair complex pieces of equipment). Relevant instructions for equipment maintenance are superimposed over cyber-representations of the assets and presented to technicians and field engineers.
Remote maintenance facilitates Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) to support their customers without having to travel on-site. Thus, it saves engineering resources and travel costs for OEMs while ensuring faster maintenance and repair processes.
Wrapping Up Predictive Maintenance
The extraction of predictive asset insights enables developing many value-added functionalities that improve maintenance processes and help professionals optimize their decisions regarding assets inspections, equipment repairs, and field service engineering activities.
The rise of Industry 4.0 leads to a proliferation of such applications in settings like smart buildings, production plants, manufacturing floors, and oil refineries. Overall, predictive maintenance is considered one of the “killer” applications of Industry 4.0 for a variety of reasons:
- It applies to most organizations, including those that manage industrial, business, governmental, and residential installations in many sectors like manufacturing, energy, oil & gas, mining, construction, smart buildings, and smart cities.
- It can be effectively combined with other Industry 4.0 applications like digital automation and digital twins to enable value-added enterprise maintenance functionalities (e.g., remote maintenance and optimal maintenance planning).
- It can be applied to almost all enterprise assets, provided that they are equipped with proper sensors.
At the dawn of Industry 4.0, industrial enterprises are considering a transition from preventive to predictive maintenance. Disruptive Technologies provides a host of enabling technologies.
The Most Comprehensive IoT Newsletter for Enterprises
Showcasing the highest-quality content, resources, news, and insights from the world of the Internet of Things. Subscribe to remain informed and up-to-date.
New Podcast Episode

IoT in 2026: Trends and Predictions
Related Articles